Homework Help Overview
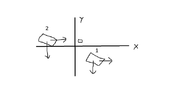
The discussion revolves around a physics problem involving a block sliding up a wedge. The problem includes elements of kinetic energy, momentum, and energy conservation, but lacks specific details such as the wedge's base length and the exact wording of the question. Participants express confusion about the setup and the definitions of variables involved.
Discussion Character
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants discuss the kinetic energy of both the block and the wedge, questioning the validity of assumptions made about their motion. Some suggest using conservation of momentum and energy, while others express uncertainty about the problem's wording and the implications of certain variables.
Discussion Status
The discussion is ongoing, with various interpretations being explored. Some participants have offered hints and guidance on potential approaches, such as using conservation laws, while others have raised concerns about the clarity of the problem statement and the definitions of variables.
Contextual Notes
There are ambiguities in the problem's wording, particularly regarding the initial conditions of the block and wedge. Participants note the lack of certain information, such as the wedge's base length, which may be critical for solving the problem.