Homework Help Overview
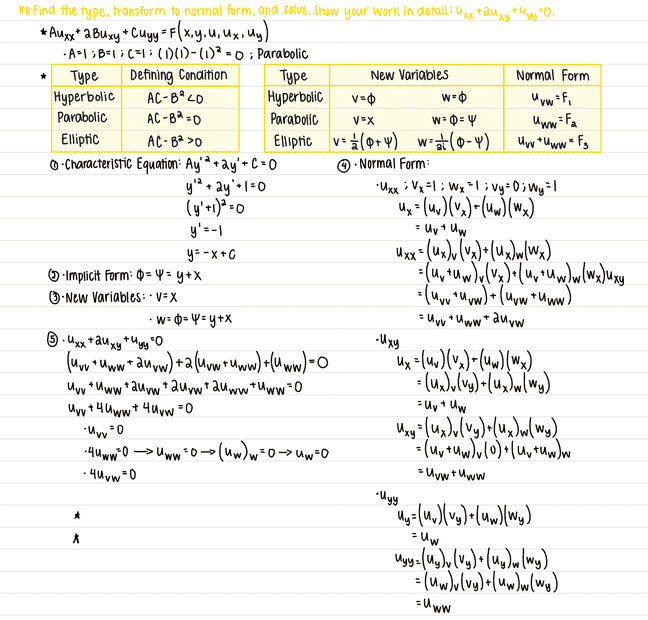
The discussion revolves around solving a partial differential equation (PDE) for the function u(x,y) and transforming it into a normal form. Participants are exploring the implications of the equation u_{ww}=0 and its integration.
Discussion Character
- Conceptual clarification, Mathematical reasoning
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants discuss the form of the solution to the PDE, questioning the nature of the function B(v) and the constants involved. There is a focus on the interpretation of the indefinite integral of zero and its implications for the solution.
Discussion Status
The discussion is active, with participants providing insights into the form of the solution and clarifying the role of arbitrary functions versus constants. There is an acknowledgment of the need to consider A as a function of v, indicating a productive exploration of the problem.
Contextual Notes
Participants are navigating the specifics of the PDE and its transformation, with some uncertainty about the definitions and assumptions regarding the functions involved.