svrphy
- 19
- 0
Tunneling from Rectangular barrier - Exponential Decay ??
Consider the Rectangular Potential Barrier. If one solves bound state Problem in this case, wavefunctions of Exponentially Decaying and rising kind are found for the Region in the Barrier.
ψ = A eαx + B e-αx
Yet Most Books and internet sources state that the Wavefunction in the Region is just Exponentially Decaying. From Wikipedia :
Simulation here : http://www.st-andrews.ac.uk/physics/quvis/embed_item_3.php?anim_id=16&file_sys=index_phys
I just can't Understand these apperent Double Standards here. The wavefunction is assumed to be "Exponentially Decaying inside the Barrier". At the same time, the Exponentially Rising term is inevitably used in the derivation of tunneling probabilities.
Just what is Going on ??
Consider the Rectangular Potential Barrier. If one solves bound state Problem in this case, wavefunctions of Exponentially Decaying and rising kind are found for the Region in the Barrier.
ψ = A eαx + B e-αx
Yet Most Books and internet sources state that the Wavefunction in the Region is just Exponentially Decaying. From Wikipedia :
From Hyperphysics:Note that, if the energy of the particle is below the barrier height, k_1 becomes imaginary and the wave function is exponentially decaying within the barrier (en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rectangular_potential_barrier)
But the wavefunction associated with a free particle must be continuous at the barrier and will show an exponential decay inside the barrier. (http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/quantum/barr.html)
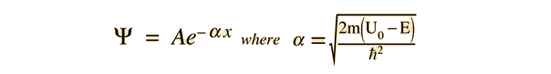
Simulation here : http://www.st-andrews.ac.uk/physics/quvis/embed_item_3.php?anim_id=16&file_sys=index_phys
I just can't Understand these apperent Double Standards here. The wavefunction is assumed to be "Exponentially Decaying inside the Barrier". At the same time, the Exponentially Rising term is inevitably used in the derivation of tunneling probabilities.
Just what is Going on ??