- #1
nchin
- 172
- 0
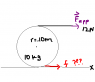
In Figure, a constant horizontal force Fapp of magnitude 12 N is applied to a uniform solid cylinder by fishing line wrapped around the cylinder. The mass of the cylinder is 10 kg, its radius is 0.10 m, and the cylinder rolls smoothly on the horizontal surface.
(a) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the center of mass of the cylinder?
(b) What is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the cylinder about the center of mass?
(c) In unit-vector notation, what is the frictional force acting on the cylinder?
solution from my teacher:
forces: Fapp + f = ma (eq'n 1)
torque: (F-f)R = 1/2MR^(2)(a/R)--->Fapp - f = 1/2ma (eq'n 2)
To solve for (a) he simply added eq'n 1 + eq'n 2.
3 things i don't understand:
When I was doing (a), I had no idea that frictional force was involved because the questions says rolls smoothly on the horizontal surface. It doesn't mention friction until part (c). So why is friction used to solve part (a)?
Also, Why is friction force at the same direction as the Fapp? I thought friction force was always opposite the Fapp??
Since, friction and Fapp are moving in the same direction, why is it then, for the torque, Fapp - f? friction and Fapp are moving in the same so shouldn't torque be Fapp + f?
(a) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the center of mass of the cylinder?
(b) What is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the cylinder about the center of mass?
(c) In unit-vector notation, what is the frictional force acting on the cylinder?
solution from my teacher:
forces: Fapp + f = ma (eq'n 1)
torque: (F-f)R = 1/2MR^(2)(a/R)--->Fapp - f = 1/2ma (eq'n 2)
To solve for (a) he simply added eq'n 1 + eq'n 2.
3 things i don't understand:
When I was doing (a), I had no idea that frictional force was involved because the questions says rolls smoothly on the horizontal surface. It doesn't mention friction until part (c). So why is friction used to solve part (a)?
Also, Why is friction force at the same direction as the Fapp? I thought friction force was always opposite the Fapp??
Since, friction and Fapp are moving in the same direction, why is it then, for the torque, Fapp - f? friction and Fapp are moving in the same so shouldn't torque be Fapp + f?