SUMMARY
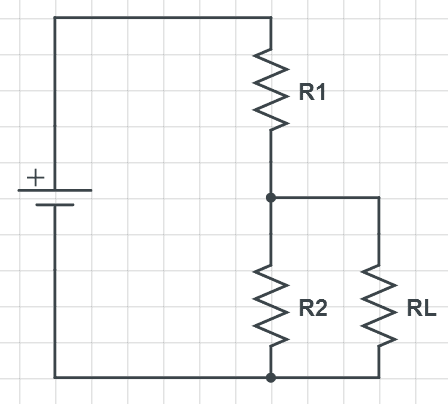
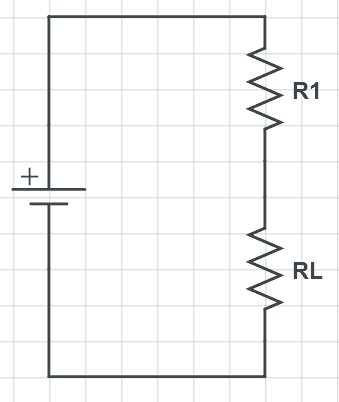
This discussion clarifies the differences between voltage dividers and voltage regulators. Voltage dividers are suitable for low-current applications, such as signal processing in digital logic, but waste power when used for significant current loads. In contrast, voltage regulators, particularly buck and boost topologies, provide efficient voltage regulation by dynamically adjusting output based on load conditions. The consensus is that voltage regulators should be preferred for applications requiring stable voltage outputs, especially when load resistance varies.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic electrical circuits and components
- Knowledge of voltage divider and voltage regulator concepts
- Familiarity with linear, buck, and boost regulator topologies
- Awareness of load resistance effects on voltage outputs
NEXT STEPS
- Research the efficiency differences between linear and switching voltage regulators
- Learn about the design principles of buck and boost converters
- Explore practical applications of voltage dividers in signal processing
- Study the impact of load resistance on voltage stability in circuits
USEFUL FOR
Electronics engineers, circuit designers, and hobbyists interested in power management and voltage regulation techniques.