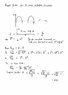SUMMARY
The ripple factor in a half-wave rectifier is defined as the ratio of the root mean square (RMS) current in alternating current (AC) to the average current in direct current (DC). The RMS current is calculated as I / √2, while the average current is I / π. The correct ripple factor value is 1.21, contrary to the incorrect calculation of 2.2 presented in the discussion. This discrepancy highlights the importance of understanding the definitions and formulas related to ripple factor in rectifier circuits.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of AC and DC current characteristics
- Knowledge of half-wave rectifier circuits
- Familiarity with RMS and average current calculations
- Basic electrical engineering principles
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of ripple factor in rectifier circuits
- Learn about full-wave rectifier ripple factor calculations
- Explore the impact of load resistance on ripple factor
- Investigate filtering techniques to reduce ripple in DC output
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and professionals working with rectifier circuits who need to understand ripple factor calculations and their implications on circuit performance.