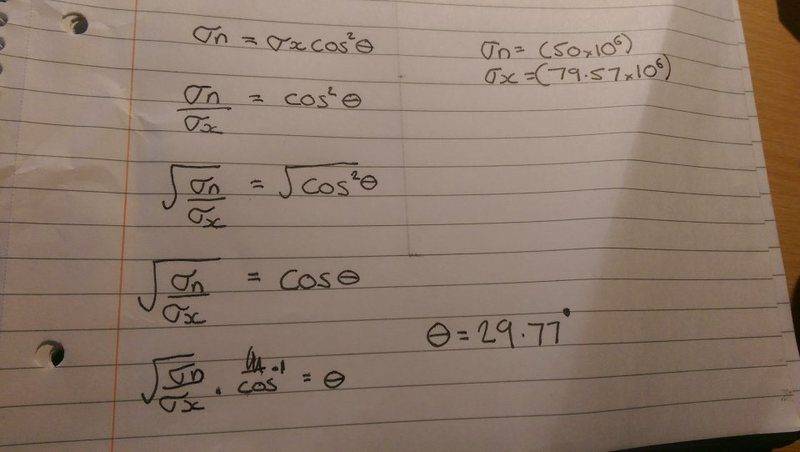SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on calculating the angle theta when the cosine has been squared, specifically using the equation ##\frac{\sigma_n}{\sigma_x} = \cos^2(\theta)##. Participants clarify that to isolate theta, one must use the inverse cosine function, expressed as ##\cos^{-1}(\theta)##, rather than multiplying by the inverse cosine. The calculated angle is approximately 37.6 degrees, with an alternative solution yielding around 142 degrees. Accurate notation and understanding of inverse functions are emphasized for correct calculations.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of trigonometric functions, particularly cosine and inverse cosine.
- Familiarity with mathematical notation, including ##\cos^2(\theta)## and ##\cos^{-1}(\theta)##.
- Basic algebra skills for manipulating equations.
- Knowledge of angle measurement in degrees.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the properties of inverse trigonometric functions, focusing on ##\cos^{-1}##.
- Practice solving equations involving squared trigonometric functions.
- Explore the concept of multiple solutions in trigonometric equations.
- Learn about the unit circle and its application in determining angle values.
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in mathematics, physics, or engineering who need to solve trigonometric equations involving squared angles and inverse functions.