SUMMARY
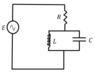
The discussion focuses on the phasor diagram of an LCR circuit, specifically addressing the relationships between the currents in the capacitor, inductor, and resistor. It is established that the currents in the capacitor and inductor are indeed parallel but point in opposite directions due to their connection in parallel. The resistor's current is the vector sum of the capacitor and inductor currents, which raises questions about its direction. Additionally, the complexity of impedance (Z) as a frequency-dependent complex number is highlighted, challenging the notion of current as a scalar.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of LCR circuit fundamentals
- Knowledge of phasor representation in AC circuits
- Familiarity with complex impedance (Z) in electrical engineering
- Basic vector addition principles in electrical contexts
NEXT STEPS
- Study phasor diagrams in AC circuit analysis
- Learn about complex impedance and its frequency dependence
- Explore vector addition of currents in parallel circuits
- Investigate the role of reactance in LCR circuits
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and professionals analyzing AC circuit behavior and phasor relationships.