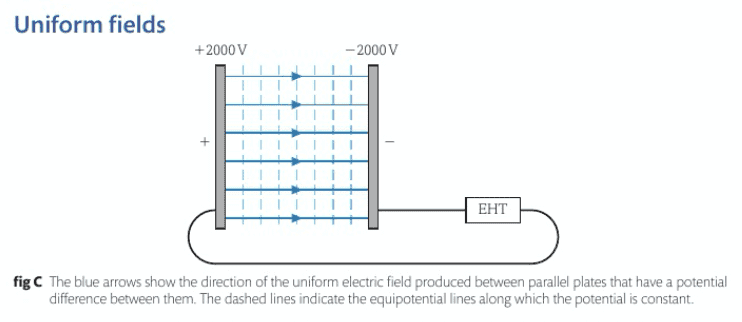
Discussion Overview
The discussion centers around the nature of electric field lines in a uniform electric field, particularly how these lines can be parallel despite being generated by multiple point sources that create radial fields. Participants explore the relationship between radial fields and the formation of parallel field lines, considering the underlying physical principles and analogies.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
Main Points Raised
- Some participants propose that the uniform field is created by multiple charged atoms acting as point sources, which generate radial fields that do not inherently produce parallel field lines.
- Others suggest that the vector sum of these radial fields results in the formation of parallel field lines in the region between the plates.
- A participant draws an analogy with wave propagation, indicating that the summation of circular waves from adjacent sources can lead to a more linear wave front, which may help explain the parallel nature of the field lines.
- It is noted that on the edges of the plates, the field lines may bulge outward, indicating a deviation from perfect parallelism at those points.
- Another participant emphasizes that the charges on the plates are fixed, leading to fields that are perpendicular to the surface, reinforcing the idea that the vector sum results in a uniform field.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express various viewpoints on how parallel field lines arise from radial fields, and while some analogies are shared, there is no consensus on the exact mechanism or implications of these observations.
Contextual Notes
The discussion includes assumptions about the behavior of electric fields and the nature of charge distribution on the plates, which may not be fully resolved. The analogy with wave propagation introduces additional complexity that is not universally accepted among participants.