Qzit said:
Hi DaleSpam,
Let's see you are saying the photon physically hits the back of the ship before the one in front hits in the Earth frame. Then they physically hit at the same time in the ships frame. Do you understand how absurd that sounds? The photon has to be in two places at the same time.
The point is that "at the same time" means something different for the Earth frame than it does for the Ship frame. Events that the two frames
can agree happen at the same time are those that happen at the same point (for example, the light hitting one end of the ship and the reading on the clock at that end of the ship at that instant.)
For demonstration here is the classic train example for the Relativity of Simultaneity.
First, events according to the embankment frame:
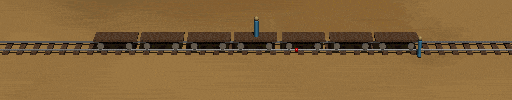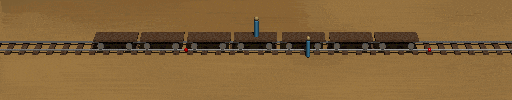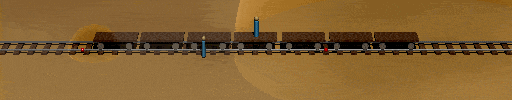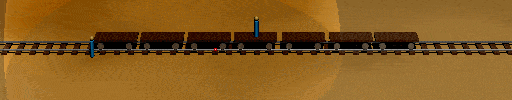
Here the lightning flashes originate when the ends of the train are adjacent to the red dots on the embankment and the embankment observer is at the midpoint between the two.
The embankment observer sees both flashes at the same time, and being halfway between the lightning strikes concludes that they occurred at the same time. Notice how the flashes reach the train observer at different times.
Now the thing to keep in mind is that in this frame, the train is length contracted, and it it this length contraction that allows it to just fit in between the two dots on the embankment.
Now the same scenario according to the Train frame. In this frame, the train is its proper length and it is the embankment which is length contracted. Now the train is longer than the distance between the two dots. The front of the train hits the right red dot before the rear reaches the left dot. The lightning strikes must originate when the ends of the trains are aligned with the dots, otherwise you will have a contradiction between the frames.
This means that in a very real sense, the lightning strikes occur at different times in the train frame. If the light from those flashes expand outward at c relative to the train, the train observer will see each flash at different times (just as he did according to the embankment frame. ). The reverse argument is that since he sees the flashes at different times, is halfway between the ends of the train(where the lightning strikes occurred) and the light from the strikes approaches him at the same speed from both ends (the speed of light is invariant), then the lightning strikes occurred at different times.
You will also note that in the train frame, the flashes also reach the embankment observer at the same time. Further, if you compare the two animations, you will note that the train observers position with respect to the embankment when each flash reaches him is the same in both as is the embankment observer's position with respect to the train when the flashes reach him.
Thus there are no true contradictions between the frames, only a disagreement as to what is simultaneous when it come to events that are separated by some distance. Note that this is not just a matter of one observer being further from the source and seeing it later, because each observer accounts for his distance from the source to determine when the flash really occurred. It is a very real difference in the simultaneity of events separated by distance.
This is length contraction and the Relativity of Simultaneity working together. If you were to place clocks at the red dots, the ends of the trains and with each observer (with the clocks in each frame synchronized in that frame), you could include time dilation into the mix, and find that everyone will agree as to what times were on any two clocks when those clocks passed each other, or when the light from either strike hit them. They will not agree as to the synchronization of clocks between frames (each frame claiming their own clocks as being in sync while the other frame's clocks are not), nor as to the relative clock rate between frames. (each will consider the clocks in the other frame as running slow.)
This is what Special Relativity is about, there are
real differences in time and space between inertial frames.
 Opps.
Opps.