Firepanda
- 425
- 0
Firstly, I don't get why the at term on the exponential turned positive (red arrow).. can someone explain that please?
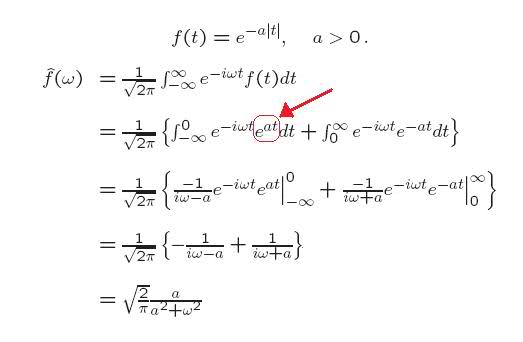
And how do I start on this? How do I split it up such that I can do it for t>0 and t=<0?
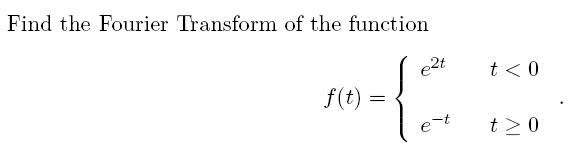
Do I just integrate e^2t between -inf and 0 and integrate e^-t between 0 and inf?
Thanks!
And how do I start on this? How do I split it up such that I can do it for t>0 and t=<0?
Do I just integrate e^2t between -inf and 0 and integrate e^-t between 0 and inf?
Thanks!