- #1
likephysics
- 636
- 2
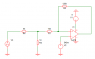
I have a comparator ckt with external hysteresis. When I apply a square wave input everything works fine. The trip points are as designed, output goes high/low etc.
But when I increase the duty cycle of the square wave to say beyond 75%, the output just stays high.
I was playing with the hysteresis resistor values. When I reduce the resistor values (and keep the same ratio), the comparator output responds to duty cycles higher than 75%.
Same is true when i decrease the duty cycle.
The comparator I am using is Microchip 6564. However this behaviour not limited to just this device. (please ignore the part number in the attachment).
I don't understand what's causing this behaviour.
But when I increase the duty cycle of the square wave to say beyond 75%, the output just stays high.
I was playing with the hysteresis resistor values. When I reduce the resistor values (and keep the same ratio), the comparator output responds to duty cycles higher than 75%.
Same is true when i decrease the duty cycle.
The comparator I am using is Microchip 6564. However this behaviour not limited to just this device. (please ignore the part number in the attachment).
I don't understand what's causing this behaviour.