- #1
jeanius
- 11
- 0
Homework Statement
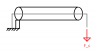
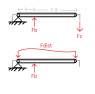
I was hoping you'd be able to help me out with a mechanics question. This isn't a homework question, more an independent design question, so the information on the problem will be primarily symbolic. I'm trying to model the force that the cable passing through the cylinder (pic) has on each segment of the cylinder, ie a distributed force. The cylinder has a number of other forces acting on it that will contribute to deflection, but I've aligned the reference frame with the cyl's neutral axis such that any rotation about the pin joint can be ignored. The force/length that the wire will exert on a length of the cylinder will depend on the cylinder's radius of curvature equation:
1/rho(x) = M(rho(x), x, F...)/EI
I've developed the moment diagram and equations for each segment of the cylinder not including the distributed force (there are forces not shown), but I'm having issues figuring out how to model the forces along the length of the cylinder due to the wire. Anyone have any idea or some concept to look up? I'm not quite sure what situation this is formally called, so if someone could identify this setup, that'd also be a big help. Oh, and the cable is fixed at the left side.
Homework Equations
I guess 1/rho(x) = M(rho(x), x, F...)/EI
Sum(Fy) = 0
Sum(Fx) = 0
The Attempt at a Solution
I've been trying to work through this conceptually, thinking that the forces exerted by the wire in the x (cylinder length) and y (vertical, modeling this as 2D) axes sum to 0, and that Fc = 1/2 * Int(Fdist(x)), but am a little apprehensive that this is the right path to take. If anyone has any advice, I'd appreciate it!