- #1
sting10
- 12
- 0
Hey, this is not a homework question really but more a research issue my fellow students and I have run into.
So basically, we have a project where we have cross-linked glucose oxidase to a polypyrrole surface on a gold electrode. The solution additionally contain PBS as well as ferricyanide as a mediator. The electrode with polypyrrole and GOX is the working electrode.
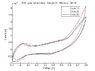
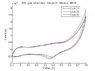
We run several laps of cyclic voltammetry and at cycle 16, we add glucose. We run several of these experiments at several concentration. three cycles have been handpicked, with 30mM and 40mM glucose have been added for your viewing.
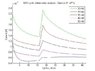
Now we analyse how the current output at 0.6V(forward scan) depends upon glucose addition when we add it at the beginning of cycle 16 (-0.1V forwards scan), which is the third image. (scan rate is 150mV/s)
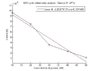
The last image illustrates the peak current when we add glucose compared to right before.
The problem we are facing is that lower concentrations of glucose added results in a higher output peak relative to higher concentration. This seems pretty counter-intuitive since we would think that a higher conc. of ferricyanide would get reduced at higher conc. of glucose which would lead to a greater oxidation current. We are thinking that there is something kinetics based that we are overlooking.
Hopefully, you have some ideas.
So basically, we have a project where we have cross-linked glucose oxidase to a polypyrrole surface on a gold electrode. The solution additionally contain PBS as well as ferricyanide as a mediator. The electrode with polypyrrole and GOX is the working electrode.
We run several laps of cyclic voltammetry and at cycle 16, we add glucose. We run several of these experiments at several concentration. three cycles have been handpicked, with 30mM and 40mM glucose have been added for your viewing.
Now we analyse how the current output at 0.6V(forward scan) depends upon glucose addition when we add it at the beginning of cycle 16 (-0.1V forwards scan), which is the third image. (scan rate is 150mV/s)
The last image illustrates the peak current when we add glucose compared to right before.
The problem we are facing is that lower concentrations of glucose added results in a higher output peak relative to higher concentration. This seems pretty counter-intuitive since we would think that a higher conc. of ferricyanide would get reduced at higher conc. of glucose which would lead to a greater oxidation current. We are thinking that there is something kinetics based that we are overlooking.
Hopefully, you have some ideas.