- #1
ApolloEngineer
- 1
- 0
Hello, I'm a senior ME student and for part of my project I'm designing a gas cooler, and I need help understanding the heat transfer process going on (I have yet to taken heat transfer).
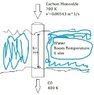
So basically my design is a a metal pipe (AISI 302 Steel k=15.1 W/m-k) carrying the gas (which for simplification purposes can be assumed to be pure Carbon Monoxide gas with a volumetric flow rate of 0.00549 m^3/s) which is surrounded by water at room temperature. What I am trying to achieve is lowering the temperature of the gas from 700K to 400K.
The main dimension I am focused on finding is how long this section of tube submerged in water must be to provide sufficient heat transfer for what I want. I know this will be a function of the inner and outer diameter of the pipe, but I am ok including those variables in some kind of final expression.
As I understand it, convection will occur on both surfaces of the pipe and conduction through the pipe wall. I have no idea how to calculate the convection coefficients, or how to take into account how this system will operate through time (this gas cooler can be expected to be run with the above conditions for up to ~6 hours), or how to model the cylindrical pipe.
Any help is much appreciated! Thanks!
So basically my design is a a metal pipe (AISI 302 Steel k=15.1 W/m-k) carrying the gas (which for simplification purposes can be assumed to be pure Carbon Monoxide gas with a volumetric flow rate of 0.00549 m^3/s) which is surrounded by water at room temperature. What I am trying to achieve is lowering the temperature of the gas from 700K to 400K.
The main dimension I am focused on finding is how long this section of tube submerged in water must be to provide sufficient heat transfer for what I want. I know this will be a function of the inner and outer diameter of the pipe, but I am ok including those variables in some kind of final expression.
As I understand it, convection will occur on both surfaces of the pipe and conduction through the pipe wall. I have no idea how to calculate the convection coefficients, or how to take into account how this system will operate through time (this gas cooler can be expected to be run with the above conditions for up to ~6 hours), or how to model the cylindrical pipe.
Any help is much appreciated! Thanks!