- #1
gabby_w
- 2
- 0
Hi everyone,
So I feel sort of stupid posting what you'll probably find is a very elementary question but physics really isn't my best subject and I'm completely stumped. Thanks so much!
Oh, and there's also the possibility that this question is just really badly worded.
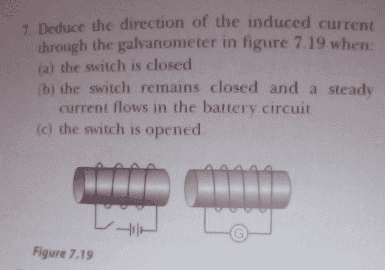
It's a question based simply on theory, not really any equations involved that could help with the answer I don't think..
I was unaware that you could induce a current in a coil without a magnet... So I have no solutions?
So I feel sort of stupid posting what you'll probably find is a very elementary question but physics really isn't my best subject and I'm completely stumped. Thanks so much!
Oh, and there's also the possibility that this question is just really badly worded.
Homework Statement
Homework Equations
It's a question based simply on theory, not really any equations involved that could help with the answer I don't think..
The Attempt at a Solution
I was unaware that you could induce a current in a coil without a magnet... So I have no solutions?