- #1
aaaa202
- 1,169
- 2
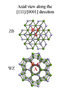
I found the following picture of the Wurtzite and Zincblende structure as viewed from a specific direction. I could do with some help on which basis vectors are chosen for either the [1 1 1] or [0 0 0 1]. Now I am pretty sure that the last one refers to a basis where we have three vectors separated by a 120degree angle in the plane and then one vector along the c-axis of the hexagonal crystal. But I don't see what other system of basis vectors you would choose to make [1 1 1] match [0 0 0 1]. Because that's what [1 1 1]/[0 0 0 1] means here right? - that they are reprsenting the direction on the picture in two different bases.