- #1
swirly90
- 8
- 0
I have a few question regarding Acceleration, I am not sure exactly how to get average acceleration from a acceleration vs. time graph. Do you make a slope? I drew a sample graph, say get the average acceleration from 11s - 25s? Would you try to draw a slope between the two time intervals?
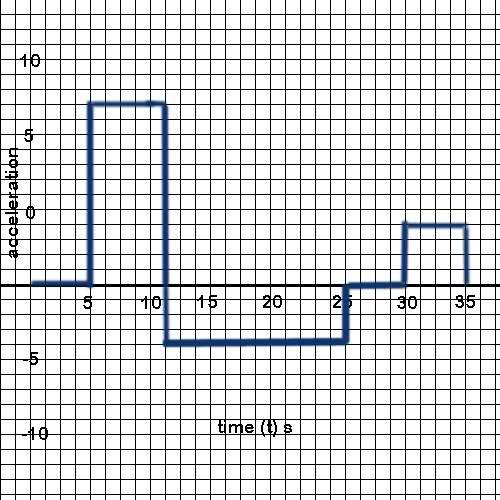
How do you find velocity on a graph like this? Is the area from the line to the zero line?
Thanks for your help.
How do you find velocity on a graph like this? Is the area from the line to the zero line?
Thanks for your help.