You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Bohr: Definition and 210 Discussions
Niels Henrik David Bohr (Danish: [ˈne̝ls ˈpoɐ̯ˀ]; 7 October 1885 – 18 November 1962) was a Danish physicist who made foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922. Bohr was also a philosopher and a promoter of scientific research.
Bohr developed the Bohr model of the atom, in which he proposed that energy levels of electrons are discrete and that the electrons revolve in stable orbits around the atomic nucleus but can jump from one energy level (or orbit) to another. Although the Bohr model has been supplanted by other models, its underlying principles remain valid. He conceived the principle of complementarity: that items could be separately analysed in terms of contradictory properties, like behaving as a wave or a stream of particles. The notion of complementarity dominated Bohr's thinking in both science and philosophy.
Bohr founded the Institute of Theoretical Physics at the University of Copenhagen, now known as the Niels Bohr Institute, which opened in 1920. Bohr mentored and collaborated with physicists including Hans Kramers, Oskar Klein, George de Hevesy, and Werner Heisenberg. He predicted the existence of a new zirconium-like element, which was named hafnium, after the Latin name for Copenhagen, where it was discovered. Later, the element bohrium was named after him.
During the 1930s Bohr helped refugees from Nazism. After Denmark was occupied by the Germans, he had a famous meeting with Heisenberg, who had become the head of the German nuclear weapon project. In September 1943 word reached Bohr that he was about to be arrested by the Germans, and he fled to Sweden. From there, he was flown to Britain, where he joined the British Tube Alloys nuclear weapons project, and was part of the British mission to the Manhattan Project. After the war, Bohr called for international cooperation on nuclear energy. He was involved with the establishment of CERN and the Research Establishment Risø of the Danish Atomic Energy Commission and became the first chairman of the Nordic Institute for Theoretical Physics in 1957.
View More On Wikipedia.org
Bohr developed the Bohr model of the atom, in which he proposed that energy levels of electrons are discrete and that the electrons revolve in stable orbits around the atomic nucleus but can jump from one energy level (or orbit) to another. Although the Bohr model has been supplanted by other models, its underlying principles remain valid. He conceived the principle of complementarity: that items could be separately analysed in terms of contradictory properties, like behaving as a wave or a stream of particles. The notion of complementarity dominated Bohr's thinking in both science and philosophy.
Bohr founded the Institute of Theoretical Physics at the University of Copenhagen, now known as the Niels Bohr Institute, which opened in 1920. Bohr mentored and collaborated with physicists including Hans Kramers, Oskar Klein, George de Hevesy, and Werner Heisenberg. He predicted the existence of a new zirconium-like element, which was named hafnium, after the Latin name for Copenhagen, where it was discovered. Later, the element bohrium was named after him.
During the 1930s Bohr helped refugees from Nazism. After Denmark was occupied by the Germans, he had a famous meeting with Heisenberg, who had become the head of the German nuclear weapon project. In September 1943 word reached Bohr that he was about to be arrested by the Germans, and he fled to Sweden. From there, he was flown to Britain, where he joined the British Tube Alloys nuclear weapons project, and was part of the British mission to the Manhattan Project. After the war, Bohr called for international cooperation on nuclear energy. He was involved with the establishment of CERN and the Research Establishment Risø of the Danish Atomic Energy Commission and became the first chairman of the Nordic Institute for Theoretical Physics in 1957.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
V
Is the Energy Change in a Bohr Atom Always Equal to One Photon?
From Wikipedia, the following diagram explains the energy emitted when an electron jumps from a higher-energy shell to a lower-energy shell: I already know that the energy of a single photon is equal to ##hf## and in this diagram, ##\Delta E=hf##. Does that mean that ##\Delta E## is only one...- Vishera
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
P
Using Bohr quantization rules to calculate energy levels
Homework Statement Use the Bohr quantization rules to calculate the energy levels for a particle moving in a potential \begin{equation} V\left(r\right)= V_0 \left(\frac{r}{a}\right)^k \end{equation} where k is positive and very large. Sketch the form of the potential (done) and show that the...- pdxautodidact
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
F
Derive an expression of Bohr radius in gravitational case
Homework Statement Both Newton's gravitational law and Coulomb's law are inverse-square laws: The force of attraction between the sun (S) and Earth(E) has (G*m_S*m_E)/r^2, whereas the force of attraction between an electron and a proton in a hydrogen atom is (e^2)/(4*pi*epsilon_0*r^2). Derive...- Frioz
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
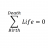
Spin/angular magnetism Bohr magneton quantum thing
So I want to get this whole spin/angular magnetism Bohr magneton quantum thing straight. Suppose a diamagnetic sphere lies at the origin. Let's talk in the x-y space for simplicity. Let's bring a bar magnet in along the x-axis approaching zero from the right. If the north pole of a bar magnet...- STEMucator
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
Y
Intro Quantum Mechanics: Neils Bohr Model Explained
Recently, I saw a video on Introductory Quantum Mechanics. Here's the link : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5Gnqpbge3Yk I failed to understand the explanation of de Broglie's model. He mentions that the waves interfere with each other but how do we know the properties like amplitude etc. of...- Yashbhatt
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr Bohr model Model
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
N
Bohr's atomic model and Bohr and Rydberg equations
Hello, well, I am totally new to this section of physics so my question may sound ridiculous, but here it is: When I was reading about the Bohr's atomic model, I learned about the Bohr and Rydberg equations (E=-2,18*10^18*Z^2/n^2 J and 1/λ=RZ^2(1/n1^2-1/n2^2) as well as their proofs. Then I...- Nick Jackson
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Atomic Atomic model Bohr Model
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-

Bohr Model Problem (Part 2 - Updated)
Greetings again, So I realize my last thread: https://www.physicsforums.com/showthread.php?t=757685 became chaotic with my thoughts and un-clear writing. I've re-did the work to make it easier for people to understand my thought process. The two questions are as follows: 7)Calculate the...- RJLiberator
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr Bohr model Model
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-

Help with the Bohr Model Problem
Okay, I am in need of some guidance: 7)Calculate the wavelength that corresponds to an emission of energy of 1.977x10^-19 J. Okay, well here is my thought process initially: Change in Energy = hc/wavelength. First question: Is 1.977*10^-19 THE change in energy? OR is that the Energy...- RJLiberator
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr Bohr model Model
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
E
Probability distribution of an electron - comparing to Bohr
Homework Statement The ground sate of a Hydrogen-like atom is given by the wavefunction: $$R_{10}(r)= 2\left(\frac{Z}{r_0}\right)^{3/2}e^{Zr/r_0}$$ and the Probability distribution is $$P(r)=4\pi r^2 |R_{10}|^2$$ At what distance is the most probable radius of the electron? Homework...- Emspak
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
T
Bohr Model of the Hydrogen atom: Prove that Eo = 13.6 eV
Homework Statement Verify that the equation of the ground state energy Eo of the Bohr atom: Eo= (2pi2e4mek2)/h2 simplifies to Eo = 13.6 eV. Show clearly how the units of the different quantities in the equation simplify to the eV. This is all they give. Nothing more...- TRE
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-
M
Magnitude of the current flowing around the nucleus in the Bohr mode
magnitude of the "current" flowing around the nucleus in the Bohr mode Homework Statement According to the Bohr model, a hydrogen atom in its lowest energy state has a nucleus consisting of a single proton, which is orbited by a single electron. The speed of the electron is 2.19×106 m/s and... -
Z
Electron energy levels in Bohr model
Homework Statement At the bottom of this linked-to screen below is an equation for E = - ... = - .... = - 13.6 Z^2 / n^2 eV https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bohr_model#Electron_energy_levelsHomework Equations I'm using the following values for the formula Z=1 n=1 K sub e = 8.987 x 10^9...- ZedCar
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
G
Bohr model and quantum model
Please excuse for my less knowledge in the subject.But I have genuine inquisitiveness. My Question is: If we assume electrons traveling in the orbit around nucleus like planets by inverse square law then electron must always be in the plannar path i,e. never coming out of plane of motion.Then...- gianeshwar
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr Bohr model Model Quantum
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
L
Finding n in Hydrogen Atom Excitation with Bohr Model
Homework Statement A hydrogen atom in an excited state absorbs a photon of wavelength 410 nm. What were the initial and final states of the hydrogen atom. Homework Equations Rydberg equation: \frac{1}{λ}=R_∞(\frac{1}{n{_l}{^2}}-\frac{1}{n{_u}{^2}}) The Attempt at a Solution...- leroyjenkens
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr Bohr model Model
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
S
Using Generalization of Bohr Rule for 1D Harmonic Oscillator
Homework Statement The generalization of the bohr rule to periodic motion more general than circular orbit states that: ∫p.dr = nh = 2∏nh(bar). the integral is a closed line integral and the "p" and "r" are vectors Using the generalized rule (the integral above), show that the spectrum for...- Shallac
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
L
Bohr radius of a helium ion
Homework Statement Using the Bohr model, find the atomic radius for a singly ionized He+ atom in the n = 1 (ground) state and the n = 2 (first excited) state. Then find the wavelength of the emitted photon when an electron transitions from the n = 2 to the n = 1 state.Homework Equations a_0 =...- leroyjenkens
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr Bohr radius Helium Ion Radius
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
J
Free-fall atomic model: Bohr with magnetic corrections
We still often meet Bohr classical atomic model, e.g. for nearly classical Rydberg atoms. However, this model ignores the fact that electron has very strong magnetic moment: is tiny magnet (it wasn't known when Bohr introduced his model). To understand why there are needed corrections, let us...- jarekd
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
H
Bohr Model: Energy Jump in Hydrogen Atom
Am I right in saying that in a Hydrogen atom when an electron jumps from the second orbit to the first one the energy change is more than any other possible jump (when the jump is not to the first orbit). The calculations seem to support me but it doesn't feel right. -
C
Did Bohr have a Logical Picture of Wittgenstein?
"As we all know..." (Uh-Oh...), Bohr and those Wacky Copenhageners were adamantly against trying to form "Pictures" of the emerging Quantum theory. Bohr berated Schrodinger (Who had tuberculosis!) while S was suffering in bed at the Institute, harassing S for hours - "Get rid of the pictures!"...- Charles Wilson
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
T
Valid reason to reject the Bohr model?
The Bohr model has been superseded by the Schrodinger model. The Bohr model involves electrons orbiting around a nucleus. I was thinking, it might be possible for the electrons to be knocked out of their stable orbits into some chaotic configuration. Is this a valid reason to reject the...- tade
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr Bohr model Model Reason
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
S
Calculating Energy in Helium Ion Ground State via Bohr Model
Homework Statement Consider a helium ion with 2 neutrons and 2 protons in the nucleus and 1 bound electron. Use the Bohr model with corrections for charge and mass of the nucleus. Calculate the energy in the ground state. Homework Equations m*v*r = n*(h/2*pi) The Attempt at a...- steve233
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr Bohr model Model
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
Meta-Stable States in Atoms & Lasers: Exploring Beyond Bohr & Schrodinger
Hey..!Its been a long time since I last posted..Any how I returned.. My question is about mEta stable states in atoms in Lasing Action.Wt actually these states are?And are they justifiable by Bohrs atomic model or Schrodinger Probabilistic orbits?If not then from where these additional states came?- moatasim23
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Atoms Bohr Lasers Schrödinger States
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
U
Generalization of the bohr rule for harmonic oscillators
Homework Statement The generalization of the bohr rule to periodic motion more general than circular orbit states that: ∫p.dr = nh = 2∏nh(bar). the integral is a closed line integral and the bolded letters represent vectors. Using the generalized, show that the spectrum for the...- uppiemurphy
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr Harmonic Oscillators
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
P
First Bohr Radius - Quantum and Atomic Model
Homework Statement Suppose an electron was bound to a proton, as in the hydrogen atom, but by the gravitational force rather than by the electric force. What would be the radius of the first Bohr orbit? Homework Equations r = h^2 / 4∏^2*mke^2 The Attempt at a Solution I'm not...- PeachBanana
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
R
Bohr model & relativity on large atoms?
Why Doesn't the increase in mass of the electrons, due to the relativistic correction required to prevent the calculated electron speed exceeding the speed of light, increase the mass of the atoms of the large elements? If the electrons were heavier on larger elements then the mass would diverge...- Ruptor
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Atoms Bohr Bohr model Model Relativity
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
C
Bohr model electron wavelengths
Hi I know that in the Bohr model, electrons move between energy levels, but you don't hear much about the electron's wavelength at each particular level. If we assume the orbits contain an integer multiple of wavelengths, you get the usual $$2\pi r=n\lambda,$$ so, based on the expression for...- copernicus1
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
S
Rejecting the Semiclassical Bohr Model: Examining the Uncertainty Relation
"Show that the uncertainty relation forces us to reject the semiclassical Bohr [...]" Homework Statement The problem along with the solution is attached as TheProblemAndSolution.jpg. Homework Equations Uncertainty principle/relation. The Attempt at a Solution Why is it the consideration of...- s3a
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
Neurtal hydrogen atom net electric charge and electric field at Bohr radius.
I am studying for my exam and I have run into this problem. The problem is given here http://faculty.mint.ua.edu/~pleclair/PH253/Homework/Spring_2010/HW6-7_atoms_12Mar10/HW6-7_atoms_12Mar10_SOLN.pdf"],[/PLAIN] it is #9. I don't understand why -e ≠ ∫ρdV from 0 to the bohr radius, a0. If all...- dolerka
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
A
Bohr radius and length contraction
from wikipedia - "The Bohr radius is a physical constant, approximately equal to the most probable distance between the proton and electron in a hydrogen atom in its ground state." in Planck units bohr radius (a0) = (mp/me).(1/\alpha).(lp) the 1st 2 terms of the RHS of the equation are...- apratim.ankur
- Thread
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
L
How did Bohr come up with his model before De Broglie?
Doesn't the Bohr model use standing waves as a reference? Before De Broglie's hypothesis, how did Bohr manage to assume that electrons are waves?- Lamarr
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr De broglie Model
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Quantum Interpretations and Foundations
-
A
How Do You Calculate the Wavelength of an Electron Transition in a Helium Ion?
Homework Statement He+ ion consists of a nucleus which is an alpha particle plus one orbiting electron.Hence it has a net positive charge. a)Derive an expression for the electron state energies b)what is the wavelength associated with a transition between the lowest two energy states...- amit25
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Atom Bohr Bohr model Helium Model
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Prove that the Bohr hydrogen atom approaches classical conditions when [..]
"Prove that the Bohr hydrogen atom approaches classical conditions when [. . .]" Homework Statement The problem and its solution are attached as ProblemSolution.jpg. Homework Equations E_k = chR/(n_k)^2 E_l = chR/(n_l)^2 ΔE = hc/λ hc/λ = chR[1/(n_k)^2 – 1/(n_l)^2] 1/ λ = R[1/(n_k)^2 –...- s3a
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
E
Converting EMU to Bohr Magnetons
Hi, I am currently working with a SQUID magnetometer and I am having trouble comparing my experimental results to theoretical. What I would like to do is convert the output of the SQUID which is in EMU to the number of Bohr Magnetons/ion. My understanding is that EMU is the sum of all...- Etreyu
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
M
If the bohr model of the atom is correct
so imagine a hyper-classical scenario. A single point elecrron is orbiting a point nucleus. No other charged objects are nearby. There is no em radiation from the electron. The electron orbits the nucleus in perfect circular motion. Zero orbital precession, zero uncertainty in the...- Michio Cuckoo
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Atom Bohr Bohr model Model
- Replies: 23
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
R
What are the challenges in calculating the Bohr radius?
Homework Statement the equation for the bohr radius is 4pi (permitivity of free space) * (reduced Planck constant)/ (elementrary charge)2(mass of an electron) The Attempt at a Solution let's just just focus on orders of magnitude: (10^-12 * 10^-34)/(((10^-19)^2)*(10^-31)...- robertjford80
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr Bohr radius Radius
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
D
Bohr model question - transition between first excited state and ground state
Homework Statement In a hydrogenlike ion with atomic number Z, the energies of the allowed states are given by E(n) = (-13.6eV) (Z^2/n^2) What is the wavelength asociated with the transition between first excited state and ground state of hydrogen-like helium? (He+) Homework...- daleklama
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Relativistic Bohr Atom and MacLaurin Series
Homework Statement By expanding a MacLaurin Series show that E_{n}=\epsilon_{n} - \mu c^{2} = - \frac{w_{0}Z^{2}}{n^{2}}[1+\frac{\alpha^{2} Z^{2}}{n}(\frac{1}{k}-\frac{3}{4n})] Homework Equations Through a lengthy derivation I arrived at \epsilon_{n}=\frac{\mu...- atomicpedals
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
O
Bohr Model and photon emission
I am feeling a little stupid asking this considering I am about to graduate with my BS in chemistry. But I have never given this much thought, nor do I remember learning this and I can't figure out a proper explanation. I am sure I am overlooking a simple detail, but I can not figure it out... -
A
What is the Radius of Bohr Atom Orbitals?
Homework Statement Given the numerical value of a0= 5.3X10^11m in the Bohr hydrogen atom, find the radius of the first five orbitals as well as the radius for n=100. Homework Equations Rn=a0 x n^2 The Attempt at a Solution Could it be as simple as typing in for the third orbital... -
X
Understanding Bohr Theory (Wavelengths for Electron States)
Ok, I am having some trouble with the maths regarding Bohr Theory. I understand that the orbit radius is r=n^2xa0 where a0=0.0529 and that the wavelength for an electron with l=0 (circular orbit), is λ=2∏r so for n=1, λ=6.28a0. So, following the same maths, for n=2, I get...- Xcellerator
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
C
Bohr Model of Atom: Stability Condition Explained
Eisberg and Resnick says that the condition for stability of the atom is: k Ze2/r2=mv2/r What I fail to understand is why the Z isn't square too. I mean surely you have Z electrons interacting with Z protons which which would surely give q1q2=(Ze)(-Ze)=-Z2e2? What am I missing?- connor415
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Atom Bohr Bohr model Model
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
J
Electromagnetic radiations in bohr model
Bohr model had a flaw that electrons would emit EM radiations and would spiral into the nucleus - but he just said that it wouldn't happen providing no reasons Do the modern models of atom explain - why electrons won't emit EM radiations?- jd12345
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
N
Bohr-Einstein debate: why did Bohr not simply say
Hello, We've all heard of the Bohr-Einstein debates to some degree (the essence of them being: Einstein tried to convince Bohr that the uncertainty principle is not true by claiming to have found concrete thought experiments that seemed to violate it). Bohr countered Einstein's arguments...- nonequilibrium
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr
- Replies: 37
- Forum: General Discussion
-
M
Find Bohr Radius from Approximate Potential Energy
[SIZE="3"]Homework Statement Determine an expression for the Bohr radius (a_{0} from the following approximation. The electron moves to the nucleus to lower its potential energy, V(r) = -\frac{e^{2}}{r} If the electron is in domain 0\leqr\leq\bar{r}, then we may write...- Mattszo
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
A
How did the Bohr Model improve the Quantum Mechanical Model?
Homework Statement How did the Bohr Model improve the Quantum Mechanical Model on our knowledge of electrons? Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution So far I have that the quantum mechanical model of the atom restricts the energy of the electrons to certain values called...- Atom21
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr Bohr model Mechanical Model Quantum
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
Solve Bohr Atom Problem: Find Radius, Energy, Wavelenght
Find the first radius, the energy of "connection" and the wavelenght of the first risk of Lyman series of a hydrogen atom that electron has been "replaced" for a meson with negative charge with a mass 207*electron mass. Radius: r = (h^2*n^2)/(4pi^2*e^2*k*me) we know all constants so we just...- Fabio010
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
W
Bohr Model Equations: Kinetic and Potential Energy in Hydrogen Atom
Homework Statement Write an expression relating the kinetic energy KE of the electron and the potential energy PE in the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom. (Use any variable or symbol stated above as necessary.) b) Suppose a hydrogen atom absorbs a photon of energy E, resulting in the...- Woopy
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr Bohr model Model
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
Exploring the Bohr Model: Visible Light Transitions in Li++
Bohr Model [b]1. Assuming that the wavelengths of visible light lie between about 300nm and 700nm, what transitions in Li++ (hydrogenic lithium ions, Z=3) would be visible. Identify each transition by initial and final principal quantum number n. Also identify those transitions that are also...- ChiefKeeper92
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Schrodinger Quantization VS Bohr Quantization
Homework Statement What are the similarities and differences between the quantization of angular momentum in the Schrodinger theory and in the Bohr model? Homework Equations ? The Attempt at a Solution Similarities: -In both theories, the principal quantum #, n, determines the...- awat
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Bohr Quantization Schrödinger
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
D
Calculating Kinetic & Potential Energy of a Bohr Orbit
Homework Statement A particular Bohr orbit in a hydrogen atom has a total energy of -0.85eV. What are (i) the kinetic energy of the electron in this orbit, and (ii) the electric potential energy of teh system? Homework Equations E=mc^2 KE= 1/2mv^2 E = hc/lambda The Attempt...- DBLE
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help