You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Conducting: Definition and 560 Discussions
Conducting is the art of directing a musical performance, such as an orchestral or choral concert. It has been defined as "the art of directing the simultaneous performance of several players or singers by the use of gesture." The primary duties of the conductor are to interpret the score in a way which reflects the specific indications in that score, set the tempo, ensure correct entries by ensemble members, and "shape" the phrasing where appropriate. Conductors communicate with their musicians primarily through hand gestures, usually with the aid of a baton, and may use other gestures or signals such as eye contact. A conductor usually supplements their direction with verbal instructions to their musicians in rehearsal.The conductor typically stands on a raised podium with a large music stand for the full score, which contains the musical notation for all the instruments or voices. Since the mid-19th century, most conductors have not played an instrument when conducting, although in earlier periods of classical music history, leading an ensemble while playing an instrument was common. In Baroque music from the 1600s to the 1750s, the group would typically be led by the harpsichordist or first violinist (see concertmaster), an approach that in modern times has been revived by several music directors for music from this period. Conducting while playing a piano or synthesizer may also be done with musical theatre pit orchestras. Communication is typically mostly non-verbal during a performance. However, in rehearsals, frequent interruptions allow the conductor to give verbal directions as to how the music should be played or sung.
Conductors act as guides to the orchestras or choirs they conduct. They choose the works to be performed and study their scores, to which they may make certain adjustments (such as in tempo, articulation, phrasing, repetitions of sections), work out their interpretation, and relay their vision to the performers. They may also attend to organizational matters, such as scheduling rehearsals, planning a concert season, hearing auditions and selecting members, and promoting their ensemble in the media. Orchestras, choirs, concert bands, and other sizable musical ensembles such as big bands are usually led by conductors.
View More On Wikipedia.org
Conductors act as guides to the orchestras or choirs they conduct. They choose the works to be performed and study their scores, to which they may make certain adjustments (such as in tempo, articulation, phrasing, repetitions of sections), work out their interpretation, and relay their vision to the performers. They may also attend to organizational matters, such as scheduling rehearsals, planning a concert season, hearing auditions and selecting members, and promoting their ensemble in the media. Orchestras, choirs, concert bands, and other sizable musical ensembles such as big bands are usually led by conductors.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
H
Potential in a Conducting Rod
When an induced emf is created in a conducting rod why is the resulting potential higher at the positive end of the rod? Since the electrons accumulate at the negative end of the rod then wouldn't this be the higher potential instead? Don't negative charges flow from lower to higher potential?- HAL10000
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Conducting Potential Rod
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Mechanics
-
J
Finding the potential between two charged conducting shells?
Homework Statement Suppose we have an outer shell with charge -2Q and radius b. We also have an inner shell with charge Q and radius a. what is the potential when a<r<b. Homework Equations E=kQ/r^2 V=kQ/r E=-dV/dx The Attempt at a Solution The method I have been using according...- JustinLiang
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Charged Conducting Potential
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Potential difference of a conducting pipe
Homework Statement A conducting cylindrical pipe has an inner radius Ra and an outer radius Rb. a charge q is released inside it. Assume the length of a cylinder L>>Rb. Find the potential difference between the axis of the cylinder and outer surface. Homework Equations Vb-Va=-∫E*dl...- Suziii
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
I
Hollow Conducting Sphere
A hollow, conducting sphere is initially uncharged. A positive charge, +q1, is placed inside the sphere (at the center). Then, a second positive charge, +q2, is placed near the sphere but outside it. Which of the following statements describes the net electric force on each charge? 1-There...- IWantToLearn
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
1
Ampere's law in a nonuniform conducting cylinder.
Homework Statement A long, cylindrical conductor of radius R carries a current I. The current density, J, is not uniform and is given by the equation J = br, where b is a constant. Find an expression for the magnetic field magnitude B at distance r < R and at distance r > R. Homework...- 13pr3ch4un
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
I
Surface Charge Density of a Neutral Conducting Cube
Homework Statement There is a region of space containing a uniform electric field of strength E. A neutral conducting cube with side length s is placed into this field. The cube is aligned with the field. You may assume that the electric field outside the cube is unaffected by any changes that...- inevitable08
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
Surface charge density on conducting cone with point charge inside
Homework Statement Calculate the surface charge density on a thin insulated and uncharged cone, which has a point charge inside of it on the cone axis. Furthermore, calculate the force between the point charge and the cone. Homework Equations The relevant equation is the Poisson equation...- jozegorisek
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
D
Concentric Cylindrical Conducting Shells and Capacitors
Homework Statement An infinitely long solid conducting cylindrical shell of radius a = 3.1 cm and negligible thickness is positioned with its symmetry axis along the z-axis as shown. The shell is charged, having a linear charge density λinner = -0.49 μC/m. Concentric with the shell is another...- diethaltao
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
T
Surface charge densities on two conducting plates.
Homework Statement I have attached the problem with a diagram. Homework Equations flux = EA = Qencl/εo The Attempt at a Solution I am confused about how I can find the charge densities on each surface. What I think is that the 5C will spread to both surfaces of plate one so...- theBEAST
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Charge Conducting Plates Surface
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
Infinite Sheets of Charge and Conducting Slab
Homework Statement An infinite sheet of charge is located in the y-z plane at x = 0 and has uniform charge denisity σ1 = 0.34 μC/m2. Another infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density σ2 = -0.14 μC/m2 is located at x = c = 26 cm.. An uncharged infinite conducting slab is placed...- darwin59
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Charge Conducting Infinite
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
Conducting Sphere: Uniform vs. Non-Uniform | Gauss's Law
Homework Statement What is the difference between a uniform conducting sphere and a uniform non-conducting sphere? I'm studying the Gauss's Law right now.- Cisneros778
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
T
Electric field inside a solid conducting sphere carrying charge q.
Homework Statement A solid conducting sphere carrying charge q has radius a. What is the electric field when r<a. Homework Equations EA=Qenclosed/εo The Attempt at a Solution I found it using gauss law where Q=density*V. I ended up with qr/(4pi*a3*εo)HOWEVER, my friend told me it should be...- theBEAST
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Z
Conducting sphere surrounded by insulator with dielectric constant
Homework Statement A conducting sphere of radius A has a charge +Q on it and is surrounded by an insulating material whose dielectric constant varies with radius according to εr = 2exp[-(r/a-1)]2. The dielectric has a spherical outer boundary B. Find the values of D, E, P, ρ as a function of...- zhillyz
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
A conducting wire has a resistivity
Homework Statement A conducting wire has a resistivity, ρ as a function of its length, L, given by ρ=(ρ0)(L) where (ρ0) is constant. A is the cross-sectional area of the wire. the resistance of the wire would be A) [(ρ0)(L)]/A B) (ρ0)/(2A) C) [(ρ0)(L)]/(2A) D) [2(ρ0)(L^2)]/A E)...- Jay9313
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
Simple question,finding the charge on conducting sphere?
Simple question,finding the charge on conducting sphere?? A conducting sphere of radius 1cm has a charge of 5microC is placed far away from another sphere with radius 2cm,,the two spheres are connected to each other by a thin wire ,the charge on the larger sphere is ? Answer : 3.33microC...- faqoosy
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
U
A two conducting balls electrostatics problem
Suppose there are two conducting balls of the same radius and the balls are separated by some distance. If both balls are at the same nonzero potential and the potential at infinity is zero, does a closed form formula for the potential exist? Since I can't find the problem solved anywhere I...- uniteast
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Differential Equations
-
K
Force between 2 parallel, charged, conducting sheets.
Homework Statement Two square parallel sheets with area>>distance between them have total charges of Q1 and Q2 on them. What is the force between them? Homework Equations Q1in+Q2in=0 Q1in+Q1out=Q1 Q2in+Q2out=Q2 Q1out=Q2out The Attempt at a Solution I set up 4 equations for the...- khfrekek1992
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Charged Conducting Force Parallel
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
T
Resistance between two points on the surface of conducting spherical shells
Hello, I'm trying to find a calculator or an equation that would help me determine the total electrical resistance between two points (A and B) on the surface of several concentric conductive spherical shells. The inputs for the calculation are the radii of the shells: r1, r2, r2, their...- Thorr
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

Can anti-matter be stored in super conducting magnetic cylinders?
frankly i don't know much about anti-matter or super conductors...i just read an into-level topic on anti-matter and had a thought. the main concern while developing an energy source is that its feasibility should be considered...right? and the problem with anti-matter is that it takes too much...- khurram usman
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
J
Image charge inside a conducting sphere
I think understand the concept of the "method of images" to describe a conductor. The conductor has to be an equipotential or else electrons would be moving around inside it. This equipotential can be described by replacing the conductor with an image charge. For example imagine the field...- johne1618
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
O
Field between 2 conducting spheres in electric field
Hi, I tried to make some simulations of two conducting spheres in a constant electric field. The simulations seem to indicate that the electric field in the gap increases with increasing diameter of the spheres at a constant gap distance. Does this make sense? I expected just the reverse. What...- oliverroth
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
L
Two conducting spheres connected by conducting wire.
Homework Statement Two spherical conductors of radii r1 and r2 are separated by a distance much greater than the radius of either sphere. The spheres are connected by a conducting wire. The charges on the sphere are in equilibrium are q1 and q2 respectively, they are uniformly charged. Find...- Legendon
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
E
Electric field of concentric conducting spheres
Why is the Qenclosed zero if there's a charge inside the shell? Homework Statement A solid conducting sphere of radius a is placed inside a conducting shell which has an inner radius b and an outer radius c. There is a charge q1 on the sphere and a charge q2 on the shell. Find the...- emr564
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Concentrical conducting spheres with charge distribution and dielectric
Hi. I have this problem, which I must solve. It says: two concentric conducting spherical shells, of radius a and b (a<b), are charged at Q and -Q respectively. The space between the spheres is filled at its half by an hemisphere of dielectric with dielectric constante ε. a)Find the field for...- Telemachus
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
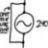
Uniformly Polarized disk on a conducting plane (E-Field)
Homework Statement A uniformly polarized dielectric disk surrounded by air is lying at a conducting plane, as shown in the figure. The polarization vector in the is, \vec{P} = P \hat{k}, the disk radius is a, and the thickness d. Calculate the electric field intensity vector along the...- jegues
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Conducting Disk E-field Plane
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

Uniformly polarized disk on a conducting plane.
Homework Statement A uniformly polarized dielectric disk surrounded by air is lying at a conducting plane, as shown in Fig. 2.36. The polarization vector in the disk is, \vec{P} = P\hat{k}, the disk radius is a, and the thickness d. Calculate the electric field intensity vector along disk...- jegues
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Conducting Disk Plane
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
Electric Field near a finite conducting stick
So this should probably go into math's section, but I feel you guys can give me the answer too, since this comes from an EE course(Theory of electromagnetic fields) http://pokit.org/get/2f3e7eef6b38bc75f0023b94976a2997.jpg(1) http://pokit.org/get/fc8658090d67ae0fafe79970021d1518.jpg(2)...- Bassalisk
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electrical Engineering
-
F
Potential difference of concentric conducting shells
My professor said to in order to solve this, integrate the electric field to find the electric potential... \Delta V = -\int\stackrel{\rightarrow}{E}dl My question is, using Gauss's Law, (\oint E_{n}dA = \frac{Q}{\epsilon}), how do I go about finding Q? Isn't Q just the charge of the shell?- faint545
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
R
Touching Conducting Spheres of Different Size
Homework Statement Two uncharged conductors A and B are of different sizes. They are charged as follows: 1. A is charged via an electrostatic generator to charge q 2. A is briefly touched to B. 3. Steps 1 and 2 are repeated until the charge on B reaches a maximum value. If the...- royblaze
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
O
EM reflection coefficient off a conducting plane
Let's say there is a conducting plane of conductivity \sigma. Boundary conditions for above and below such plane are: E_1^t = E_2^t (D_2 - D_1 ) \cdot n = \rho i.e. tangential components of E field are continuous and perpendicular components of D are discontinuous because of surface charge... -
D
Potential of Concentric Cylindrical Insulator and Conducting Shell
An infinitely long solid insulating cylinder of radius a = 5.3 cm is positioned with its symmetry axis along the z-axis as shown. The cylinder is uniformly charged with a charge density ρ = 45 μC/m3. Concentric with the cylinder is a cylindrical conducting shell of inner radius b = 14.2 cm, and...- dancingmonkey
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
P
Charge Distribution on Conducting Spherical Shell
Homework Statement A conducting spherical shell that has zero net charge has an inner radius R1 and an outer radius R2. A postive point charge q is placed at the center of the cell. The 1st part was to find the electric fields at the 3 diff places. The part I need help on is where we have to...- pyroknife
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
R
Need some clarification on conducting spheres
Question: Two identical conducting spheres, fixed in place, attract each other with an electrostatic force of 0.141 N when their center-to-center separation is 67.0 cm. The spheres are then connected by a thin conducting wire. When the wire is removed, the spheres repel each other with an...- RandellK02
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
T
Electrostatics - Conducting torus and a point charge
Homework Statement We have a metal conducting torus and a point charge that is located on the torus' axis (location on the axis is arbitrary). Calculate the (influenced) charge distribution on the torus and the electrostatic force on the point charge. Homework Equations Equation for...- thepero
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
P
Charge distribution in a conducting sphere
Homework Statement At time t = 0 a charge distribution \rho(r) exists within an idealized homogeneous conductor whose permitivity \epsilon and conductivity \sigma are constant. Obtain \rho(r,t) for subsequent times. Homework Equations Maxwell's equations = Gauss' Equation + Ohm's...- Plantis
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
Y
EM wave right above and right below the conducting surface.
Assume a infinite depth good conductor block with width in y and length in x direction. Boundary is at z=0 and air is at z=-ve and conductor at z=+ve. Let a voltage apply across the length of the block in x direction so a current density established in +ve x direction. We want to look at the EM...- yungman
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Conducting Em Em wave Surface Wave
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
S
Difference between electric field intensity of plane and conducting sheet
what is the difference between the electric field intensity of 1)infinite plane charged sheet whose formula is E=\sigma/2\epsilono and 2)infinite conducting charged sheet whose formula is E = \sigma/\epsilono- Sumedh
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
S
Charge inside conducting shell
Homework Statement Inside a metal conducting shell of radius R there is a negative charge q at a distance a from the center M. The shell is brought up to a potential V. What is the surface charge on the inside and outside of the conductor? The Attempt at a Solution I'm not sure if this...- Shukie
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Charge Conducting Shell
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Q
Square Conducting Ring - Electrodynamics Question
Homework Statement Ok I'm going through last year's practice exam for electrodynamics and I'm stuck on a particular problem. For problem statement see attachment. q5a part i is fine but I'm confused with the other parts. Homework Equations...- QuantumJG
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
P
Reflection at a conducting surface
In Griffiths Electrodynamics (page 397) electromagnetic wave reflection at a conducting surface is introduced. He says "for ohmic conductors, Jfree = sigma * E, there can be no free surface current since this would require an infinite electric field at the boundary." I don't understand why...- phrygian
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Conducting Reflection Surface
- Replies: 23
- Forum: Optics
-
R
Electric potential of a charged dielectric-coated conducting cylinder
Homework Statement We have an infinitely-long perfect electrical conductor (PEC) cylindrical core (Region 3) of radius a surrounded by a dielectric layer (Region 2) of permittivity ε2 and radius b. The combined conductor/dielectric cylinder is embedded in an infinite space (Region 1) of...- rsheldon86
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
E
Electric potential of a conducting sphere
Homework Statement A 5.5 cm radius conducting sphere is charged until the electric field just outside its surface is 1667 V/m. What is the electric potential of this sphere, relative to infinity? Homework Equations V = - integral ( E (dot) dl ) The Attempt at a Solution They only...- elyons
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Current on Parallel Conducting Wires
Homework Statement Two very long, straight, parallel wires carry currents that are directed perpendicular to the page as shown in Figure P30.9. Wire 1 carries a current I1 into the page (in the -z direction) and passes through the x-axis at x = +a. Wire 2 passes through the x-axis at x = -2a...- aglo6509
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Conducting Current Parallel Wires
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
I
Charge at the center of a conducting sphere
If you place a charge +q at the exact center of a conducting sphere, will it stay there or move to the surface?- Idoubt
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
S
Faraday's Law vs. V = vBl for determing potential difference of a conducting rod
Homework Statement A rod rotates clockwise about a point as pivot with the constant frequency 5 rev/s. Find the potential difference between its two ends, which are 80 cm apart, due to the magnetic field B = 0.3T directed into the page. Homework Equations There are two methods to find...- sdcmma
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
Electron flow over a conducting surface of variable resistivity
Hello fellow physics-people, I was just thinking about the following setup: We have a conducting surface (with smoothly varying resistivity) hooked up to some battery with the wires contacting the surface at two arbitrary points, A and B. How would we go about figuring out the current...- fyzxfreak
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
N
Electric Field around Conducting Surfaces
Hey, Completing AP Problems, I ran into a puzzling answer. Basically, there was a conducting sphere with charge Q on it and radius R1, and then around it two hollow hemispheres were placed (forming a spherical capacitor) which had no charge, with Radius R2 at the inner edge and R3 at the...- nimadh
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
K
Can a Rotating Conducting Disk Generate a Magnetic Field?
In a recent homework problem for my physics class, there was a question regarding a non conducting disk with a charge, and this rotating disk (axis or rotation perpendicular to the surface, through the center) will produce a B field because of the movement of charges. Now suppose I have a...- khemist
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Conducting Disk Rotating
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Mechanics
-
O
Temperature of a Conducting Rod
Homework Statement A copper rod 90cm long is used to poke a fire. The hot end of the rod is maintained at 103 degrees Celsius and the cool end has a constant temperature of 25C. What is the temperature of the rod 24cm from the cool end? specific heat of copper: c = 387 J/kg*K thermal...- ObliviousSage
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Conducting Rod Temperature
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Hollow conducting sphere in external E field
Suppose I put an (uncharged) hollow conducting sphere with inner radius a and outer radius b in an external electric field in the positive z direction. Apparently, the potential INSIDE the sphere -- that is, for 0 < r < a -- is zero. Can someone explain why this is? I understand that the...- AxiomOfChoice
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Classical Physics