You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Gravitational: Definition and 1000 Discussions
Gravity (from Latin gravitas 'weight'), or gravitation, is a natural phenomenon by which all things with mass or energy—including planets, stars, galaxies, and even light—are attracted to (or gravitate toward) one another. On Earth, gravity gives weight to physical objects, and the Moon's gravity causes the ocean tides. The gravitational attraction of the original gaseous matter present in the Universe caused it to begin coalescing and forming stars and caused the stars to group together into galaxies, so gravity is responsible for many of the large-scale structures in the Universe. Gravity has an infinite range, although its effects become weaker as objects get further away.
Gravity is most accurately described by the general theory of relativity (proposed by Albert Einstein in 1915), which describes gravity not as a force, but as a consequence of masses moving along geodesic lines in a curved spacetime caused by the uneven distribution of mass. The most extreme example of this curvature of spacetime is a black hole, from which nothing—not even light—can escape once past the black hole's event horizon. However, for most applications, gravity is well approximated by Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes gravity as a force causing any two bodies to be attracted toward each other, with magnitude proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Gravity is the weakest of the four fundamental interactions of physics, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong interaction, 1036 times weaker than the electromagnetic force and 1029 times weaker than the weak interaction. As a consequence, it has no significant influence at the level of subatomic particles. In contrast, it is the dominant interaction at the macroscopic scale, and is the cause of the formation, shape and trajectory (orbit) of astronomical bodies.
Current models of particle physics imply that the earliest instance of gravity in the Universe, possibly in the form of quantum gravity, supergravity or a gravitational singularity, along with ordinary space and time, developed during the Planck epoch (up to 10−43 seconds after the birth of the Universe), possibly from a primeval state, such as a false vacuum, quantum vacuum or virtual particle, in a currently unknown manner. Attempts to develop a theory of gravity consistent with quantum mechanics, a quantum gravity theory, which would allow gravity to be united in a common mathematical framework (a theory of everything) with the other three fundamental interactions of physics, are a current area of research.
View More On Wikipedia.org
Gravity is most accurately described by the general theory of relativity (proposed by Albert Einstein in 1915), which describes gravity not as a force, but as a consequence of masses moving along geodesic lines in a curved spacetime caused by the uneven distribution of mass. The most extreme example of this curvature of spacetime is a black hole, from which nothing—not even light—can escape once past the black hole's event horizon. However, for most applications, gravity is well approximated by Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes gravity as a force causing any two bodies to be attracted toward each other, with magnitude proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Gravity is the weakest of the four fundamental interactions of physics, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong interaction, 1036 times weaker than the electromagnetic force and 1029 times weaker than the weak interaction. As a consequence, it has no significant influence at the level of subatomic particles. In contrast, it is the dominant interaction at the macroscopic scale, and is the cause of the formation, shape and trajectory (orbit) of astronomical bodies.
Current models of particle physics imply that the earliest instance of gravity in the Universe, possibly in the form of quantum gravity, supergravity or a gravitational singularity, along with ordinary space and time, developed during the Planck epoch (up to 10−43 seconds after the birth of the Universe), possibly from a primeval state, such as a false vacuum, quantum vacuum or virtual particle, in a currently unknown manner. Attempts to develop a theory of gravity consistent with quantum mechanics, a quantum gravity theory, which would allow gravity to be united in a common mathematical framework (a theory of everything) with the other three fundamental interactions of physics, are a current area of research.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
M
B Gravitational Lensing: Magnification of Galaxies
How many time does a galaxy (same size as our milkyway) magnified the background ?- Mikael17
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Acceleration at 1g in space -- Does it create a gravitational field?
Does a body accelerating at 1g in outer space create a gravitational field around it ?- BigyanAdhikari
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Mechanics
-
K
I Gravitational Field with Dark Energy: Observable Effects?
since the cosmological constant observed is that there is a small amount of energy in empty space, and in general relativity anytime there is energy there is curvature and therefore gravity, how to calculate gravitational field with dark energy and does it have any observable effects on matter...- kodama
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
A
I Gravitational vs. Electromagnetic Waves: What's the Difference?
in a nutshell what are the differences between gravitational and electromagnetic waves?- accdd
- Thread
- Replies: 20
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Frequency of Gravitational Waves: Limit & Possibilities
A question elsewhere got me thinking about the frequencies/wavelengths of gravitational waves. The most obvious source of gravitational waves we are finding is from merging black holes, so presumably the orbital period will directly determine the frequency of those waves, yes? So the...- DaveC426913
- Thread
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Exploring Gravitational Waves with Earth-Lunar Orbital Perturbations
Hello, This article caught my attention recently and I have several questions on the subject that I'd like to get opinions on. Before going further, I realize a technical discussion is way past the "I" tags range. Please adjust as necessary and thank you in advance. My attention was originally...- Oldman too
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
B Gravitational acceleration in circular motion
Hi guys, I have a question that is simple but I do not know how to answer that. It is the following, where does the acceleration of 9,8 meters per second squared go when We're dealing with uniform circular motion? I know that We have the centripetal acceleration that is a vector change, but the...- physicsmagician
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Mechanics
-
B Why exactly do we need the gravitational constant?
That may seem like a silly question, but suppose the crew of an interstellar vessel wanted to measure the mass of their ship, perhaps to estimate remaining resources. Unless they have very well calibrated thrust and a very well calibrated accelerometer, the only option is to do so...- Keith Koenig
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
N
I Curved space and gravitational waves
Are gravitational waves purely temporal? An object with no spatial velocity experiences gravity due to temporal velocity?- Nidhi1007
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
Gravitational Field and Potential at certain point
The removed mass is ##\frac{1}{8}M## My idea is to find ##g## from large sphere then minus it with ##g## from small sphere (because of the removed mass): ##g## at A = $$\frac{GM}{R^3}\left(\frac{1}{2}R\right)-\frac{G\left(\frac{1}{8}M\right)}{R^2}$$ Is this correct? Thanks- songoku
- Thread
- Replies: 20
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Alien spaceship wormhole gravitational waves detector
Recently viewed video about wormholes that required negative energy to create it. Suppose hypothetical aliens have discovered this technology. Spaceship enters in first point and exit at second. To prevent spaceship destruction they might have technology to smooth gravitational waves on exit...- Dinarchik
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Science Fiction and Fantasy Media
-
G
I Information content in electromagnetic or gravitational waves
Electromagnetic or gravitational wave carries energy and momentum from place to place as,I understand.Does it imply that such waves only can carry information and if their energy gets dissipated as heat, the information contained is lost. Is this information content is to be decoded by human...- gianeshwar
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
S
I Gravitational force equation derived from GR
Hello everyone, I know that GR equations are complicated and beyond my scope. But does GR give a simple gravitational equation: Force (as we know it) as a function of distance? (without any complicated tensors). - If yes. What is the equation? Does it give us something similar to Newtons...- sha1000
- Thread
- Replies: 36
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
B Clock Ticking in Gravitational Well: Observation Rate
I was wondering what someone standing far away from a planet with mass would see if he drops a clock towards the mass. And then vice versa if I was standing on the planet, what would I see. would I see the clock tick fast and then slow as it approaches? Thanks!- sqljunkey
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Clock Gravitational Rate
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
I
B Gravitational Orbits: How the Earth Knows Where to Go
How does the Earth's reference frame "know" to experience the gravitational pull of where the sun/Earth barycenter will be in 8 minutes, rather than orbit around the spot where the barycenter was 8 minutes ago? The latter case seems required by the finite speed of gravitation, but coplanar...- InkTide
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Earth Gravitational Orbits
- Replies: 29
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
Gravitational potential energy traveling from earth to mars
My attempt: Let ##M_e## be the mass of the Earth and ##M_m## be the mass of the person. Let ##D_{EM}## be the distance from Earth to Mars and let ##R_e## be the radius of the earth. Defining these constants (leaving off units for brevity): Masses in Kilograms (G is not a mass but I'll leave...- ago01
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

B Gravitational Force acting on a massless body
It's a well known fact that acceleration due to gravity is independent of the mass of the accelerating body, and only depends on the mass of the body it is accelerating towards and the distance from it. One can prove this mathematically very easily. F=GMm/r^2 (equation 1) but also F=ma...- Lunct
- Thread
- Replies: 67
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
U
Help with a calculation about gravitational waves
An exact gravitational plane wave solution to Einstein's field equation has the line metric $$\mathrm{d}s^2=-2\mathrm{d}u\mathrm{d}v+a^2(u)\mathrm{d}^2x+b^2(u)\mathrm{d}^2y.$$ I have calculated the non-vanishing Christoffel symbols and Ricci curvature components and used the vacuum Einstein...- user1139
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
Gravitational Forces between two masses
Density of the Sphere = 3M/4πR³ Mass of carved out sphere = density × 4π/3 × R³/8 = M/8 The position of center of mass of The Sphere {M(0) - M/8(R/2)}/M-M/8 -R/14 So total distance between centers of the two bodies is R/14 + 3R = 43R/14 So now I found force between the Mass 7M/8 (left out...- SpectraPhy09
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
I Gravitational Illusions -- Two balls rolling down differently-shaped ramps
Without this test,using only math, would you prove that left ball will comes first?- Jurgen M
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Balls Gravitational Rolling
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
M
I On the gravitational collapse of a massive shell
Black holes form. An undeniable fact. Let's imagine a massive shell collapsing under its own weight (the exact composition of the mass is not important, so just imagine to be a continuous mass with zero thickness). What happens if the process of collapse evolves? The time on the inside will run...- Mattergauge
- Thread
- Replies: 45
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
I
Calculate gravitational acceleration without mass of both objects
I haven't gotten anywhere. I don't find it possible to calculate this since Fg varies based on the Mass of the meteroide and because of that it will change acceleration. I thought about trying to remove m1 by making F=m*a the same as 𝜸(m1*m2)/r^2 since I think they are the same force. m*a=...- IAmBadAtMath
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
H
I Image for increase in gravitational potential energy in radial field
A question to physicists: What sort of real world scenario / image would *best* depict the increase in gravitational potential energy in a radial field? Would a rocket traveling through the Earth's atmosphere suffice or are there better alternatives? This image would have to be relevant to the...- hexcalibur
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-

Gravitational force equals centrifugal force?
Book says that correct answer is d) but I can't understand why. If the result of gravitational and centrifugal force is 0N then there is no force that would keep those objects inside the spacecraft orbiting around the planet. Or am I just completely wrong? Thank you for your help.- Induana
- Thread
- Replies: 23
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I Exploring the Speed of Light: Gravitational Waves
Why are gravitational waves able to move at the speed of light?- brucegoth123
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
B
I Why aren't Gravitational waves factored in to inflation formulas?
It seems to me that gravitational waves are ignored when inflationary physics are described. I'm not very well read, and honestly do not know so much about most of the physics going on with inflation. Still, wave mechanics matter, harmonics matter, and it just seems intuitive to me that in order... -

B Finding Gravitational Acceleration
Hi if I understand it correctly, this is the process to find freefall acceleration of a falling body. S=ut+1/2at^2 Initial time and displacement is zero so, S=1/2at^2 find acceleration a=2(S/t^2) graph for change in displacement over time squared a= 2(yf-yi/xf-xi) (f=final i= initial) I...- Martyn59
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
A
I How do gravitational waves differ from the expansion of the Universe?
How do gravitational waves in spacetime stretch and compress solid matter such as the LIGO experiment. I ask this because the expansion of spacetime of the Universe doesn't seem to have any effect on the small scale ie the solar system.- Andy DS
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
L
Gravitational force - I translating the wording into the formula
i spoke to my proffesor about it but all he said was to put 1 in m1 and m2... for r^2 since it says to quadruple to just put 4^2 I asked about the G in the equation but he said not to worry about iit and pretend its not there...- lesdayy
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
I Gravitational Field of Electromagnetic Waves: How is it Generated?
Hi ! It catches my attention that atomic particles such as protons, neutornes, electrons and their respective subparticles such as Quarks are theoretically formed by high-energy electromagnetic fields such as gamma rays and then the gravitational field that would generate the mass of these...- MartinG
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Detecting Gravitational Waves w/ Interferometers: Explained
Hi, I would like to ask for some clarification about the physics involved in the gravitational waves detection using interferometers. Starting from this thread Light speed and the LIGO experiment I'm aware of the two ends of an arm of the interferometer (e.g. LIGO) can be taken as the...- cianfa72
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
I Merging black holes: gravitational waves and information
A popular theory is that black holes gradually leak information because of black hole evaporation due to hawking radiation. When black holes merge, a significant portion of their mass is converted into gravitational waves. If it's true that black holes leak information due to hawking radiation...- arusse02
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
R
Misunderstanding of Gravitational Potential Energy
Here is my solution, which is correct. The tilt of the water at the top can be described in terms of ##x## and ##y## as ##y = \frac{2y_0}{L}x##. The height of the water at any given x is then equal to ##h + \frac{2y_0}{L}x## where ##x \in [-\frac{L}{2}, \frac{L}{2}]##. So the potential...- Rsch613
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
B Question about the solar system and gravitational forces
Alright, so I have a question. Now, on planets such as our Earth, there are a longitude and latitude as well as altitude. If I am not mistaken, I believe the latitude and altitude are part of what affects gravity, or weight, on a planet. Latitude makes it so that the object in question is...- Sundown444
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
I
I Kinetic vs Gravitational Time Dilation: Perceived Speed
As an object approaches a black hole’s event horizon, it experiences increasing gravitational time dilation, causing it to appear to an outside observer to slow down, until, at the event horizon, it appears to stop. An object traveling in space that increases its velocity from one...- Involute
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Rindler Transformation & 't Hooft's Introduction to General Relativity
I am reading 't Hooft introduction to general relativity. https://webspace.science.uu.nl/~hooft10 ... l_2010.pdf In this text 't Hoof derives the Rindler transformation. A little bit further he writes My question is, how does he come to that formula $$\rho^{-2}g(\zeta)$$- wnvl2
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Gravitational potential of an ellipsoid
There is a formula for the potential ##\varphi## outside of a homogenous ellipsoid of density ##\mu## in Landau\begin{align*} \varphi = -\pi \mu abck \int_{\xi}^{\infty} \left(1- \dfrac{x^2}{a^2 + s} + \dfrac{y^2}{b^2 + s} + \dfrac{z^2}{c^2+s} \right) \frac{ds}{R_s} \ \ \ (1) \end{align*}where...- ergospherical
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
B ARC Centre reports HF Gravitational Wave Antenna
The full title of the publication is: Rare Events Detected with a Bulk Acoustic Wave High Frequency Gravitational Wave Antenna It is published in Physics Review Letters and reported in Phys Org. They have created a small piezo-electric device (< 2cm, though it gets bigger once you create an...- .Scott
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
M
I Time Dilation in Gravitational Fields vs Acceleration on Earth
If I'm standing on Earth, is my time dilation actually greater than if I was in a rocket accelerating at 9.8m/s^2 in deep space due to me being in a gravitational field on top of the acceleration? Geodesics experience time dilation in gravitational fields, so it seems like there is an additive...- mcgnms
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Why used $\cos\theta$ for $\text{y}$ axis or, gravitational force?
>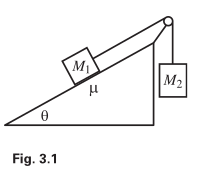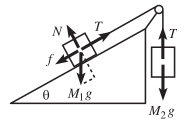<br/> >Mass M1 is held on a plane with inclination angle θ, and mass M2 hangs over the side. The two masses are connected by a massless string...- Istiak
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

A Some questions about the derivation steps in the Gravitational deflection of light section in Schutz
In the screenshots below there are the equations (11.49) and (11.53). I don't understand how did he derive equation (11.53) from Eq.(11.49)? From (11.49) I get: ##d\phi/dy= d\phi/du du/dy = (1/b^2-u^2+2Mu^3)^{-1/2}(1+2My)##. It seems he neglected the ##2Mu^3## since ##Mu\ll 1##, so ##y\approx...- MathematicalPhysicist
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Do Gravitational Forces Increase for Objects Moving at Light Speed?
Since an object's apparent mass increases as it approaches the speed of light, does it's gravitational forces also increases? (From a stationary observer's point of view)- Pratyeka
- Thread
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Exact Integration of Newton's Gravitational Law?
I realized I never actually derived the kinematic equations of motion for the exact Newtonian gravitational force. For an object falling near the surface of the earth, how do we handle integrating the equation of motion to derive the kinematics equations without using the approximation of...- bob012345
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Gravitational Integration Law
- Replies: 25
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

B Gravitational Lensing: Refraction or Something Else?
It seems like a strong gravitational field acts like spacetime is denser in some sense. Light passing through a gravitational lens is delayed, just like in a glass lens (which refracts because it's denser than air).- Paige_Turner
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
B Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution under the influence of a gravitational field
Could anyone suggest a simple video showing the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution under the influence of a gravitational field? I trying to show a flat earther idiot how pressure gradients arise in a simple manner. Thank you all. DF- merlyn
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
E
I Does charging my phone increase its gravitational force?
If the statement above is correct, I do not understand this concept. I guess by charging my phone I am not producing matter. Does it mean in this case, energy converts to mass (not matter)? Can someone please explain this?- Ebi
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Find GR Equation: Collapsing Orbit & Gravitational Wave
I recall some time ago seeing a GR equation describing the rate of orbital energy loss from the moving objects in orbit generating gravitational waves. I can no longer find this equation again. I am hoping someone can help me.- Buzz Bloom
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
B
Gravitational Potential In the Field Caused by Two Masses
I got (a) but have no idea about b. Potential fields aren't just additive all the time are they?- BrandonInFlorida
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

B Gravitational force between matter and antimatter
What is the current scientific consensus on the gravitational force between matter and antimatter. Is it repulsive, attractive or zero?- Delta2
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
E
A Cosmological gravitational waves
The exercise is to derive the form of the symmetric, trace-free and transverse gravitational wave perturbation ##\hat{E}_{ij}## to the FRW metric$$ds^2 = a^2(\tau) \left[ -d\tau^2 + (\delta_{ij} + 2\hat{E}_{ij})dx^i dx^j \right]$$First step is to figure out the connection coefficients, which are...- etotheipi
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Cosmology