You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Ligo: Definition and 97 Discussions
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) is a large-scale physics experiment and observatory designed to detect cosmic gravitational waves and to develop gravitational-wave observations as an astronomical tool. Two large observatories were built in the United States with the aim of detecting gravitational waves by laser interferometry. These observatories use mirrors spaced four kilometers apart which are capable of detecting a change of less than one ten-thousandth the charge diameter of a proton.The initial LIGO observatories were funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and were conceived, built and are operated by Caltech and MIT. They collected data from 2002 to 2010 but no gravitational waves were detected.
The Advanced LIGO Project to enhance the original LIGO detectors began in 2008 and continues to be supported by the NSF, with important contributions from the United Kingdom's Science and Technology Facilities Council, the Max Planck Society of Germany, and the Australian Research Council. The improved detectors began operation in 2015. The detection of gravitational waves was reported in 2016 by the LIGO Scientific Collaboration (LSC) and the Virgo Collaboration with the international participation of scientists from several universities and research institutions. Scientists involved in the project and the analysis of the data for gravitational-wave astronomy are organized by the LSC, which includes more than 1000 scientists worldwide, as well as 440,000 active Einstein@Home users as of December 2016.LIGO is the largest and most ambitious project ever funded by the NSF.
In 2017, the Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Rainer Weiss, Kip Thorne and Barry C. Barish "for decisive contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves".Observations are made in "runs". As of December 2019, LIGO has made 3 runs, and made 50 detections of gravitational waves. Maintenance and upgrades of the detectors are made between runs. The first run, O1, which ran from 12 September 2015 to 19 January 2016, made the first 3 detections, all black hole mergers. The second run, O2, which ran from 30 November 2016 to 25 August 2017, made 8 detections, 7 black hole mergers, and the first neutron star merger. The third run, O3, began on 1 April 2019; it is divided (so far) into O3a, from 1 April to 30 September 2019, and O3b, from 1 November 2019 until it was suspended in March 2020 due to COVID-19.
View More On Wikipedia.org
The Advanced LIGO Project to enhance the original LIGO detectors began in 2008 and continues to be supported by the NSF, with important contributions from the United Kingdom's Science and Technology Facilities Council, the Max Planck Society of Germany, and the Australian Research Council. The improved detectors began operation in 2015. The detection of gravitational waves was reported in 2016 by the LIGO Scientific Collaboration (LSC) and the Virgo Collaboration with the international participation of scientists from several universities and research institutions. Scientists involved in the project and the analysis of the data for gravitational-wave astronomy are organized by the LSC, which includes more than 1000 scientists worldwide, as well as 440,000 active Einstein@Home users as of December 2016.LIGO is the largest and most ambitious project ever funded by the NSF.
In 2017, the Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Rainer Weiss, Kip Thorne and Barry C. Barish "for decisive contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves".Observations are made in "runs". As of December 2019, LIGO has made 3 runs, and made 50 detections of gravitational waves. Maintenance and upgrades of the detectors are made between runs. The first run, O1, which ran from 12 September 2015 to 19 January 2016, made the first 3 detections, all black hole mergers. The second run, O2, which ran from 30 November 2016 to 25 August 2017, made 8 detections, 7 black hole mergers, and the first neutron star merger. The third run, O3, began on 1 April 2019; it is divided (so far) into O3a, from 1 April to 30 September 2019, and O3b, from 1 November 2019 until it was suspended in March 2020 due to COVID-19.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
I
B Could you use LIGO-technology to measure gravitational redshift?
Don't know if this is the right forum, but I'll give it a try: If you build a bridge over a gorge that's a couple km deep the middle of the bridge would be as far away from the mountains on both sides as possible (and therefore as far away from the mountains' gravitational field as possible)...- Isambard
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B LIGO Back Online: Upgraded Detector to Spot Fainter Gravitational Waves
From this morning's Economist briefing: The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory—the world’s most sensitive device for spotting gravitational waves—starts up again on Wednesday after a three-year hiatus for upgrades. LIGO is designed to detect subtle ripples in space and time...- phinds
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
I LIGO: Detecting Differences Less Than a Proton Length - How is It Possible?
I read that the LIGO detector in the US was able to detect a difference of less that the length of a proton, or maybe even less than this. How is this possible? The perpendicular arms won't be the same length down to the nearest proton length. Also, at such small lengths the microclimate on each...- thegroundhog
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
Z
I LIGO & Special Relativity: Is Spacetime Distortion Real?
Hello Is the distortion of spacetime by gravitational waves directly related to the contraction of objects in motion predicted by special relativity ? In other words Besides the existence of the gravitational waves , did the LIGO experiment definitely confirm the contraction of the bodies in...- zoltrix
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
B
I LIGO -- Direction of sensing
As I understand, the gravity wave detection system is possible due to the change in length of the two arms, as a wave passes, thus changing the distance the light beams travel. As this distance changes, the time of flight will change in relationship to each other. This difference is then...- Bern1937
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
R
B LIGO Arm Length & Sensitivity: What's the Relation?
[Moderator's note: Spun off from previous thread due to new question.] I have read here: http://backreaction.blogspot.com/2016/02/everything-you-need-to-know-about.html?m=1 That there is a proportionality between the size of LIGO arms and the wavelength of gravitational waves that it can...- roineust
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Arm Length Ligo Relation Sensitivity
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
R
B Modern Cavendish vs LIGO: Gravity Scale & Wave Interruption?
What is the scale of magnitude of gravity, that a modern Cavendish like laser detector of gravity pull between small daily size objects can detect in comparison to the magnitude of gravitational wave a LIGO like detector can detect? Will such a modern Cavendish like device measurements be...- roineust
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Device Ligo Scale Sensitivity
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

LIGO India is hosting a series of live talks on Youtube
LIGO India EPO (Education and Public Outreach) team is hosting a series of talks on Youtube. No registration or any formalities; just tune into the LIGO India EPO Youtube channel and you can attend the lectures. Following is the list of upcoming talks: 20th April: Speaker: Prof. Ajith...- Wrichik Basu
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: General Discussion
-
K
I Ligo Heat Dissipation: How Do They Protect Mirrors?
Hello! I am not sure I understand how the heat from the lasers get dissipated in LIGO, at the mirrors. Given the high power of the lasers, the mirrors heat up, but the setup is in vacuum, so it is difficult to get rid of that heat. How do they make sure that the mirrors don't get too much damage...- kelly0303
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Dissipation Heat Ligo
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I LIGO Gravitational Wave Detection News
Here is the most recent one:- Wrichik Basu
- Thread
- Replies: 26
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
H
Other How do I find the list of individual LIGO participants?
This link https://www.ligo.org/about.php and this link https://my.ligo.org/census.php show me the list of participating universities in LIGO. I am currently doing research under a professor at my university who is a member of LIGO. Neither of the above links lists the names of the individual...- Henry Shi
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: STEM Academic Advising
-
P
B How does the LIGO experiment affect SpaceTime?
I'm just a layperson with a keen interest a couple of notches above popular science. As far as I understand SpaceTime is an attribute where if you change one attribute (space or time) then the other attribute is affected. E.g. as you approach the speed of light, the time passing of other things...- physicsnoobie79
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Experiment Ligo Spacetime
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
B LIGO and space time changes
Sorry if the question has been already answered, but I didn't manage to find it. Let's go back to ligo detection of gravitational waves, my question is the following: if space time changes its texture due to a gravitational effect, all the rulers (and clocks) in that spot will be affected, so...- asca
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ligo Space Space time Time
- Replies: 67
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
I Can the LIGO observatories detect (with accuracy) temblors?
With all the earthquakes going on in CA - and that the last one (7.1 mag) was strong enough to possibly trigger a small quake along the LA coast (i.e., as in LouisianA, not Los Angeles) - I was wondering about this. These instruments are so sensitive that they have to pick something up, even in...- swampwiz
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
N
How does Quadruple Pendulum isolate LIGO from Seismic Vibrations?
On 28 November 2018, a lecture was given by Dr. Rainer Weiss (2017 Nobel Prize Winner for Physics) at the Ontario Science Centre, Toronto. The lecture was about his work with the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO). In his lecture talked about quadruple pendulums or... -

I Why can't LIGO detect collisions of super massive black holes?
Does anyone know, and is there an instrument that could?- mitosis
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Collisions Holes Ligo
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Cosmology
-
Physics Is gravitational wave research a smart direction to go in?
Is it a fair prediction to state that in the next several years or so, globally, there will be major investments into gravitational wave research, and many more ‘LIGOs’ being developed? Is it a good idea to venture into that area of physics?- astroman707
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: STEM Career Guidance
-
Courses Academic Preparation for gravitational wave careers?
If someone wanted to pursue a career in gravitational wave physics, and work at places like LIGO, studying astrophysical objects such as black holes and neutron stars, etc. What are some key courses/skills that person should take/learn as an undergraduate, and graduate student?- astroman707
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: STEM Academic Advising
-

B LIGO's Detection of Gravitational Waves: BH-BH & BH-NS Mergers
Since it's detection of GW150914, How many BH BH mergers has it detected and how many BH NS mergers has it detected, Is it living up to the potential detection's that are predicted?- wolram
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ligo
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

B LIGO Observation of Gravitational Waves: Questions Answered
I am doing a term paper on G. Waves and I have a couple of questions about them. - How do we know that the G. Waves detected by LIGO on September 14, 2015, come from 1.5 billion light years? - How is Einstein's Theory related to them?- Andrew Washington
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Collision of two black holes
This computer simulation shows the collision of two black holes, as observed for the first time ever by the LIGO on September 14, 2015. The black holes in the animation are based on the actual data from the collision as detected by LIGO. (Simulating eXtreme Spacetimes (SXS) Project (http://www.black- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- ligo
- Comments: 0
- Category: Astronomy and Cosmology
-
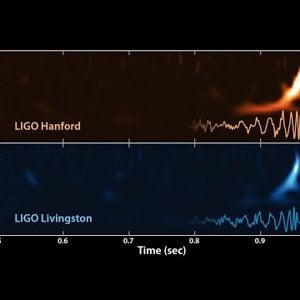
First LIGO detected gravitational wave signal converted into audible form
On September 14, 2015 LIGO made scientific history by detecting gravitational waves for the very first time. The signal received by LIGO was converted into an audible sound.- Wrichik Basu
- Media item
- ligo
- Comments: 0
- Category: Astronomy and Cosmology
-
H
B Why does a LIGO arm stretch and not move in unison?
LIGO is most sensitive to a GW from directly above/below. As a transverse wave hits an arm why don't the laser source and the mirror move in unison -- thereby covering up the distorted motion?- Henri Garcia
- Thread
- Replies: 46
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B What Are the Benefits of LIGO & VIRGO's Gravitational Wave Detection?
I mean do they only detect gravitational waves?, if yes then why spending so much money on this big machine, just to detect something(i know that proving such a beautiful theory is a great achievement), but what next, i mean what other benefits they got after detecting gravitational waves- parshyaa
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ligo
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
A
B Gravitational Wave Stretching: LIGO Arm vs Light
I'm puzzled that the stretching of space by a gravitational wave stretches the LIGO arm but not the light within it. Because we are told that the red shift of a distant galaxy is caused by light being stretched by the expansion of space (the universe).- Alfred Cann
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
A
B How does LIGO measure gravitational waves
I'm aware that the LIGO system uses interferometry but I'm confused how it works in this case. Do they test both beams of light? Or do they use one beam to test the wavelength of the other and see the difference? Also it is sensitive up to 10 e-18 meters, is that for the change in wavelength or...- AamsterC2
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
C
B How electromagnetic stellar gravity waves (GR) form the effects of sound waves at the LIGO observatory?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LIGO#/media/File:Simplified_diagram_of_an_Advanced_LIGO_detector.png The axis on the bottom of the graph depicts frequencies between 20-1000 Hz which are sound waves. Again, how can a sound wave (gravity waves) propagate in the near vacuum of stellar space...- carl susumu
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Gravity Gravity waves Ligo Waves
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
J
I Determining Mass & Info of Merging Neutron Stars from LIGO Signal
How does one determine/calculate the masses, orbital period, and separation of two merging neutron stars from the characteristics of its gravity wave LIGO signal? And how does this information allow one to calculate the distance to the galaxy that housed the merger? And how can one calculate...- jordankonisky
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

A Falsifications and constraints due to GW measurements
This thread is to serve as - a collection of theories that have been falsified by and/or have had new constrained placed on them by the ongoing gravitational wave measurements. - a place to discuss the further constraining/falsifying of still existing models using GW data. I'll start by posting...- Auto-Didact
- Thread
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
A
I Where Did LIGO Find Merging Black Holes?
Surprisingly, I have not been able to find an answer to this question. How did scientists know where to build LIGO so that it would be able to find merging black holes in the sky? I assume LIGO is a permanent instrument so that it cannot be pointed to various parts of the sky, like an ordinary...- Albertgauss
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black holes Holes Ligo
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I LIGO: How to Know Wave Direction?
Im sure you guys see a lot of this. I only come here when google has let me down for several hours. How does LIGO know where the waves are coming from? My guess is that they can get an idea of the direction of the wave based on how the arms are stretched of compressed. Thanks.- nmsurobert
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ligo
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

MHB LIGO Announcement due Monday ....
LIGO will unveil new developments in its search for gravitational waves ... but no details as yet ... Peter- Math Amateur
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ligo
- Replies: 1
- Forum: General Discussion
-

A Penrose: Noise in LIGO signal implies CCC
Roger Penrose, July 2017. Correlated "noise" in LIGO gravitational wave signals: an implication of Conformal Cyclic Cosmology- Auto-Didact
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

A Uncovering the Truth Behind LIGO's Gravity Wave Detection: A Critical Analysis
Hi, I was looking for a second opinion on this article regarding LIGO's gravity waves and if it made sense or not. https://www.forbes.com/sites/startswithabang/2017/06/16/was-it-all-just-noise-independent-analysis-casts-doubt-on-ligos-detections "Analysis of the data attributed the signal to...- auou
- Thread
- Replies: 117
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
E
I LIGO and light speed constancy
From LIGO website re how gravity waves are measured: "The arrival times change because when the arms of the interferometer change lengths, so too do the distances the light waves travel before exiting the interferometer. What gravitational waves do not change, however, is the speed of light...- ewq
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Light Light speed Ligo Speed
- Replies: 118
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
E
How Does LIGO Detect Gravitational Waves Using Laser Interferometry?
Homework Statement In-phase light from a laser with an effective power of 2x105J and a wavelength of 1064nm is sent down perpendicular 4km arms of the LIGO detector. (i) Determine the number of photons traveling in the interferometer arms. (ii) Assuming the detector is sensitive enough to...- EGN123
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

B Can Phonon Excitations in BECs Revolutionize Gravitational Wave Detection?
Ivette Fuentes and her group are attempting to use phonon excitations in BECs to detect gravitational waves. Their GW-detector is called MAGA, which stands for Micrometre Antenna for Gravitational-wave Astronomy. Here's a video of her explaining it: More from their blog:- Auto-Didact
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
E
B LIGO: Detecting Gravity Wave Sources
I would have a question to LIGO. How can LIGO detect the source of a gravity wave? It's a 2-dimensional detector, which has a certain length and a certain width, but no height. How does LIGO know the direction and distance of the source, and if this source is on the one side of LIGO or exactly... -
A
I LIGO BH Merger & Black Hole Information Paradox
Has anyone analysed the LIGO merger detection http://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.061102 in the context of the BH information paradox? Is there any evidence that the gravitational waves carried any information that could compensate for the change in areas of the initial...- andrew s 1905
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Modeling the effects of GW and the "Earth Frame"
First let me be clear, I am not questioning GR or the detection of gravitational waves by LIGO, I am trying to improve my own understanding of GW to the point where I can offer a graphic illustration (web video) showing what they do as they pass us to help others understand them. I started this...- GeorgeDishman
- Thread
- Replies: 66
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Could LIGO Have Detected Dark Matter?
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/06/160615134951.htm From science daily Date: June 15, 2016 Source: Johns Hopkins University Summary: When an astronomical observatory detected two black holes colliding in deep space, scientists celebrated confirmation of Einstein's prediction of...- wolram
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Dark matter Ligo Matter
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Cosmology
-
E
I LIGO light changes frequency not wavelength
Gravitational wave stretches and shrinks space. Why Laser light in Ligo arms changes frequency, and not wavelength.Is it some clear explanation? If even frequency would not be changed than spacetime is not changed, I suppose. What cannot be measured, cannot exist.- exponent137
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Frequency Light Ligo Wavelength
- Replies: 105
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
E
B LIGO detects second gravity waves
http://news.mit.edu/2016/second-time-ligo-detects-gravitational-waves-0615 This seems to be the year of black holes, between LIGO, and new theories of black holes being 2D objects instead of 3D masses. Anyway, I thought this was very interesting news and wanted to share :)- elusiveshame
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Gravity Gravity waves Ligo Waves
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
V
B LIGO Detection Question: Why Lighter Masses Mean More Time
Re: the second LIGO detection, from Symmetry: “Because of their lighter masses compared to the first detection, they spent more time—about one second—in the sensitive band of the detectors.” As an absolute (albeit deeply fascinated) novice here, I'm unclear as to why lighter masses would allow...- verve825
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
M
A Was the LIGO team over-hasty to claim black holes confirmed?
Since the thread In LIGO’s pulse, how much comes from BH merging/ inspiraling where I questioned the late ‘ringdown’ part of the LIGO signal, scientists have pointed out that the main pre-merging signal could indicate various types of binary compact objects, including gravastars of similar mass...- MaxWallis
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I (How) does the LIGO experiment falsify Newtonian gravity?
Sorry for the amateurish setup that follows. Here's my thought experiment. Consider a 2-dimensional universe on the Cartesian plane. Earth is located at point (0,0). There is a binary system {A,B} oscillating around (1,1). To simplify, assume that the oscillation is 1-dimensional and occurs on...- EnumaElish
- Thread
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
M
A In LIGO’s pulse, how much comes from BH merging/ inspiraling
The inspiralling oscillations of ~20ms period (reducing to ~5ms) appear much stronger than the ringdown of ~ 3ms period (noisy, at resolution limit). Merger happens at ~440ms in the figure of Abbott et al. (Phys Res Lett link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.061102). This would agree with...- MaxWallis
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Gravitational waves Ligo Pulse
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Cosmology
-
C
B LIGO experiment Gravity waves
I read that they found gravity waves that have the frequency of 35 to 250 hz but are not these frequencies that of sound waves? I thought sound does not propagate in vacuum or is there a new kind of gravity vacuum that contains a gravity ether or dark matter?- carl susumu
- Thread
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
J
I Light speed and the LIGO experiment
Hello all, I was thinking about the speed of light and why it's constant and it brought me to the principle of the LIGO experiment for which I have an assumption that I want to verify. I'm a novice at this so please bear with me. From what I know, the LIGO experiment splits an emitting light...- JohnnyGui
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Experiment Light Light speed Ligo Speed
- Replies: 60
- Forum: Special and General Relativity