You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Magnetostatics: Definition and 77 Discussions
Magnetostatics is the study of magnetic fields in systems where the currents are steady (not changing with time). It is the magnetic analogue of electrostatics, where the charges are stationary. The magnetization need not be static; the equations of magnetostatics can be used to predict fast magnetic switching events that occur on time scales of nanoseconds or less. Magnetostatics is even a good approximation when the currents are not static — as long as the currents do not alternate rapidly. Magnetostatics is widely used in applications of micromagnetics such as models of magnetic storage devices as in computer memory. Magnetostatic focussing can be achieved either by a permanent magnet or by passing current through a coil of wire whose axis coincides with the beam axis.
View More On Wikipedia.org
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
G
Magnetostatics multiple choice
Homework Statement A charged particle traveling with a velocity v in a magnetic field B experiences a force F that must be: A. parallel to v B. perpendicular to only v C. parallel to v-B D. parallel to B E. perpendicular to v x B Homework Equations Requires this right hand...- goomer
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Electric field in magnetostatics?
Hello In magnetostatics theory, there exists a current of charges. So in this situation charges are not stationary, and the Coulomb's law, and all the relations derived from it, are not valid. My question is how can we obtain electric field when dealing with steady currents (within...- Arham
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

Magnetostatics. Calculate the magnetic flux density.
Problem description: A wery long, than and flat metal plate of width 2a carries the total current I in the z-direction. The current density is uniformely distributed over the metal plate. A point P of particular interest is also shown in the figure, where the point has the position r=ax+ay...- beyondlight
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
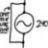
Magnetostatics - Magnetic Flux + Force
Homework Statement See figure attached. Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution I can follow how he applies amperes law to obtain the magnetic field produce by the wire but I'm extremely confused how he writes the expression for the flux flowing through S. What I...- jegues
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
Vector potential and energy calculations in magnetostatics
I have some trouble with the calculation of energy in magnetostatics, using the vector potential A. From the classic formula that uses B*H, I find the expression (in magnetostatics) in terms of A and J (current density): \begin{align}W &=\frac{1}{2}\int_V{\vec{B}\cdot\vec{H}{\rm d}V}\\...- Mbert
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
S
Magnetostatics problem: find B and H
Homework Statement A long wire carries a current I and is centered in a long hollow cylinder of inner radius a and outer radius b. The cylinder is made of a linear material with permeability \mu. Find \mathbf{B} and \mathbf{H} everywhere. Homework Equations The Attempt at a...- summerwind
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Magnetostatics
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
0
Magnetostatics boundary conditions.
I am sometimes just not sure how to go about solving magnetics problems and applying the right boundary conditions. I was hoping for a little advice. For example in an infinitely long cylinder (along z-axis) with radius a, and a permanent magnetization given by: \vec{M} =...- 0ddbio
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
P
Magnetostatics - boundary condition
Let's consider two media with magnetic permeability \mu_1, \mu_2 . What's the condition for magnetostatic vector potential \vec{A} on the boundary. Is it true that its tangent component should be continuous. Thanks for replay.- paweld
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
K
Magnetostatics: Magnetic Vector Potential
Homework Statement Give an expression for the magnetic field and show that a magnetic vector exists such as \vec{A}(P) = A(r)\hat{z} and \vec{B}(P) = \vec{\nabla} \times \vec{A} For the infinite wire shown in figure 1. Here is a link to the figure and problem statement. The problem is the...- KEØM
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
S
Magnetostatics: Proof for θi, μ1, μ2, and μ3
[PLAIN]http://img714.imageshack.us/img714/2757/96034584.png Homework Statement In the image above, magnetic flux enters the first interface of a three-layer geometry at an angle θi. If all three media are non-conducting and have permeabilities μ1, μ2, and μ3. a.) show that the angle θo...- satchmo05
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Magnetostatics Proof
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
V
Magnetostatics - force on wire
Homework Statement A segment of wire carries a current of 20 A along the x-axis from x = −6 m to x = 0 and then along the z axis from z = 0 to z = 7.2 m. In this region of space, the magnetic field is equal to 51 mT in the positive z direction. What is the magnitude of the force on this...- victorlee2
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Force Magnetostatics Wire
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
K
Magnetostatics - Rotation of circular disc
Homework Statement A disc has radius a and rotates with angular frequency w. Magnetic flux density is B. Such a disc of mass 10^4 kg and radius 3m is rotating freely at 3000 revs/min in a field of 0.5T. A load of 10^-3 ohms is connected suddenly between the rim and the axis of the disc...- Keano16
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Conducting planes in magnetostatics
Homework Statement Two infinitely long perfectly conducting planes at x = 0 and y = 0 form a boundary on the upper right quadrant (x > 0, y > 0). A magnetic dipole m = m_x + m_y [with their corresponding unit vectors] is located at at (x', y', z' = 0) in the upper right quadrant. Find the...- shehry1
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
J
Numerical methods in magnetostatics
hello, i'm wondering is there any review of most used methods in magnetostatics? and also if there are analitical solutions of distibution of magnetic field in cylindricall coordinates for: current loop, solenoid, current flown cylinder, coaxial cable and magnetic buffer (protection)...- jadelsky
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
T
Magnetostatics - magnetic flux and energy in toroidal inductor
Homework Statement A toroidal inductor consists of 500 turns of wire on a ring-shaped core of magnetic material with a relative permeability of 8000. The core has a square cross-section with an internal radius of 20mm, external radius of 40mm and height of 20mm. Find: a) Magnetic flux in the...- tigger88
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
C
Magnetostatics - Determine the magnetic field
Two wires carrying currents of 4A and 6A, respectively, are oriented perpendicular to each other and cross without electrical connection at the origin. Determine the magnetic field magnitude and direction at the point (2, 4). [bI don't even know what equation to use for this. All we have...- confusedgirl
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
L
Magnetostatics: Find B in Cylindrical Pipe w/V, \zeta, a, L
A cylindrical pipe of radius a and length L is filled with mercury of electrical conductivity \zeta. A potential difference V acts across the two ends of the pipe, creating an electric current through the mercury (which remains stationary). (i)Find the current density, assumed uniform, within...- latentcorpse
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Magnetostatics
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
D
Magnetostatics - field of a current loop
Homework Statement Find the magnetic field at the center of a square loop, which carries a steady current I. Let R be the distance from center to side.Homework Equations Biot-Savart for a steady line current: B(r) = μI∫ dl X r ---- ----------------------...- darkchild
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
T
Virtual Work - Magnetostatics - Feynman?
In reading Feynman's "Lectures on Physics", volume 2 I have a question and have included a scan of a small section from the book. Feynman was a big fan of using the Principle of Virtual Work, but his explanation, as least insofar as how he used it is wanting, at least for me. The attached...- Thomas2054
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
J
Magnetostatics and Electrostatics
Here is the problem, I have no idea how to do this! (In a single straight wire) If the positive charges (density p+) are at rest, and the negative charges (density p-) move at speed v, show that: p- = -(p+)*(gamma)^2- johanjones190
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Why does my textbook only show magnetostatics when curl of H = 0?
In my textbooks it shows curl of H = 0 is a situtaion of magnetostatics but in here http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnetostatics it shows otherwise assuming J can be anything. Which is correct? Magnetostatics is defined to be when the magnetic field is constant so H should be a vector field...- pivoxa15
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Homework Magnetostatics
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
R
Solving a Magnetostatics Integral Problem
I'm working on a physics problem, and i got stuck on an integral. the entire question is as follows: ---------------------------- Magnetostatics treats the "source current" (the one that sets up the field) and the "recipient current" (the one that experiences the force) so...- rocket
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Integral Magnetostatics
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
R
Magnetostatics Proof: Proving Integral Along a Closed Loop = 0
I'm working on a physics problem, and i got stuck on an integral. the entire question is as follows: ---------------------------- Magnetostatics treats the "source current" (the one that sets up the field) and the "recipient current" (the one that experiences the force) so...- rocket
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Magnetostatics Proof
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
H
Magnetostatics -> Electrostatics?
Magnetostatics -> Electrostatics?? I have a questions and I am afraid that I might look very dumb for asking such questions, so forgive me first. I heard many times how Maxwell's equations along with Lorents Force Law tells all the story of EM dynamics. So I wanted to see if I can show...- HungryChemist
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
H
Calculating Ampere Turns for Toroid with Air Gap: Exploring Magnetic Fields
I'm very sorry if this questions seems easy to you guys but it's been giving me a hard time. An iron ring has a uniform cross-sectional area of 150mm^2 and a mean radius of 200mm. The ring is continuous except for an air gap of 1mm wide. Calculate the ampere turns at the air gap when B=...- hiiragizawa
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Magnetostatics
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
How Does Magnetostatics Explain Zero Divergence and Vector Potentials?
Hi :) this is my first post to this forum. I am doing some study in EM and I've come across some helpful hints on here, to help me through some problems. However i have come across a couple stumbling blocks. if anyone could give me a couple clues to go about working these out and give me a...- _Syzygy_
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Magnetostatics
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Electrons in a Moving Wire: The Lorentz Force
Consider an infinate current carrying wire along the z-axis. Let I be the current in the wire and suppose that flowing electrons produce this current. The wire has no net charge density because the density of positive ions is assumed to compensate the density of flowing electrons. Let the...- scariari
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Electro Magnetostatics
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help