You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Polarization: Definition and 660 Discussions
Polarization (also polarisation) is a property applying to transverse waves that specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. A simple example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string (see image); for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves (shear waves) in solids.
An electromagnetic wave such as light consists of a coupled oscillating electric field and magnetic field which are always perpendicular to each other; by convention, the "polarization" of electromagnetic waves refers to the direction of the electric field. In linear polarization, the fields oscillate in a single direction. In circular or elliptical polarization, the fields rotate at a constant rate in a plane as the wave travels. The rotation can have two possible directions; if the fields rotate in a right hand sense with respect to the direction of wave travel, it is called right circular polarization, while if the fields rotate in a left hand sense, it is called left circular polarization.
Light or other electromagnetic radiation from many sources, such as the sun, flames, and incandescent lamps, consists of short wave trains with an equal mixture of polarizations; this is called unpolarized light. Polarized light can be produced by passing unpolarized light through a polarizer, which allows waves of only one polarization to pass through. The most common optical materials do not affect the polarization of light, however, some materials—those that exhibit birefringence, dichroism, or optical activity—affect light differently depending on its polarization. Some of these are used to make polarizing filters. Light is also partially polarized when it reflects from a surface.
According to quantum mechanics, electromagnetic waves can also be viewed as streams of particles called photons. When viewed in this way, the polarization of an electromagnetic wave is determined by a quantum mechanical property of photons called their spin. A photon has one of two possible spins: it can either spin in a right hand sense or a left hand sense about its direction of travel. Circularly polarized electromagnetic waves are composed of photons with only one type of spin, either right- or left-hand. Linearly polarized waves consist of photons that are in a superposition of right and left circularly polarized states, with equal amplitude and phases synchronized to give oscillation in a plane.Polarization is an important parameter in areas of science dealing with transverse waves, such as optics, seismology, radio, and microwaves. Especially impacted are technologies such as lasers, wireless and optical fiber telecommunications, and radar.
View More On Wikipedia.org
An electromagnetic wave such as light consists of a coupled oscillating electric field and magnetic field which are always perpendicular to each other; by convention, the "polarization" of electromagnetic waves refers to the direction of the electric field. In linear polarization, the fields oscillate in a single direction. In circular or elliptical polarization, the fields rotate at a constant rate in a plane as the wave travels. The rotation can have two possible directions; if the fields rotate in a right hand sense with respect to the direction of wave travel, it is called right circular polarization, while if the fields rotate in a left hand sense, it is called left circular polarization.
Light or other electromagnetic radiation from many sources, such as the sun, flames, and incandescent lamps, consists of short wave trains with an equal mixture of polarizations; this is called unpolarized light. Polarized light can be produced by passing unpolarized light through a polarizer, which allows waves of only one polarization to pass through. The most common optical materials do not affect the polarization of light, however, some materials—those that exhibit birefringence, dichroism, or optical activity—affect light differently depending on its polarization. Some of these are used to make polarizing filters. Light is also partially polarized when it reflects from a surface.
According to quantum mechanics, electromagnetic waves can also be viewed as streams of particles called photons. When viewed in this way, the polarization of an electromagnetic wave is determined by a quantum mechanical property of photons called their spin. A photon has one of two possible spins: it can either spin in a right hand sense or a left hand sense about its direction of travel. Circularly polarized electromagnetic waves are composed of photons with only one type of spin, either right- or left-hand. Linearly polarized waves consist of photons that are in a superposition of right and left circularly polarized states, with equal amplitude and phases synchronized to give oscillation in a plane.Polarization is an important parameter in areas of science dealing with transverse waves, such as optics, seismology, radio, and microwaves. Especially impacted are technologies such as lasers, wireless and optical fiber telecommunications, and radar.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-

Information loss in polarization.
A single photon approaches a polarization filter. It's orientation is described by a probability amplitude wave function. It is not reflected or absorbed, but passes through the filter. Now it's orientation immediately after is definitely known. Question 1: is there no...- anorlunda
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Information Loss Polarization
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
T
Photon polarization and direction
When a photon is produced when an atom raised to excited state return to ground state it's frequency can be calculated. but can we predict the direction and polarization of that photon.- TeCNoYoTTa
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Direction Photon Polarization
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Optics
-
G
Quantum interference with different polarization
Hi all, Imagine a double slit experiment where each slit contains a polarization filter with some angle relative to each other (\alpha). If the polarization filters are parallel the usual interference pattern will emerge, and when they are perpendicular no interference pattern will emerge. What... -
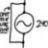
Current & Potential Polarization for Directional Relays
Hello all, I've been reading up on both potential and current polarization for directional phase relays in, "Power System Relaying" by Stanley H. Horowitz and Arun G. Phadke and I am confused as to how the direction of the fault (i.e. into or out of the line) is obtained. In potential...- jegues
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Current Polarization Potential
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electrical Engineering
-

Wave Interference and Polarization
I'm studying wave interference and having trouble to understand some concepts. I would like to ask what would happen in the 2 situations below Image 1 Image 2 Both waves are identical, have the same frequency, amplitude and velocity. They are polarized on the direction shown (first...- jaumzaum
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Interference Polarization Wave
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Optics
-
O
E-field polarization in the direction of propagation, TEM, TE, TM
I read that for a plane wave E, B and k are always perpendicular to each other but then in a TM mode I have electric field in the direction of propagation. This means this TM and TE modes I cannot have in free space? Can I have them in a laser? If I can have some E-field in the direction of... -
N
Understanding Electric Polarization in Dielectric Capacitors
Does the electric polarization density of a dielectric inside a capacitor have the same direction as the electrical field? Considering the electric dipole moment vector goes from the - charge to + charge?- Nikitin
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Electric Polarization
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
W
Photon Polarization: Linear vs Circular & Time-Dependent States
So I know that a linearly polarized photon is in a state ψ = cos(θ)\left|x\right\rangle + sin(θ)\left|y\right\rangle What if θ depends on time maybe something like θ\equiv\frac{E_{0}t}{\hbar}? The polarization is linear at any time t, it rotates as time passes? Isn't that circular...- wotanub
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Photon Polarization
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
S
Polarization by reflection and Brewsters Angle
Homework Statement A beam of light is reflected off the surface of some unknown liquid, and the light is examined with a linear sheet polarizer. It is found that when the central axis of the polarizer (that is, perpendicular to the plane of the sheet) is tilted down from the vertical at an...- Sswift
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Angle Polarization Reflection
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Why Do Photons from Electrons Split into Particles?
¿ Why the photons emitted by an electron are desintegrated in a photon, and then in an electron a positron? The positive charge stay near the electron doing that charge stay minus than its real value. But, ¿ why don´t matter the same with the mass??- StarsRuler
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Electron Polarization
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
W
QM: Neutrino Polarization - Oscillation & Mass Polarization
I was reading in my QM book that neutrinos are "essentially left handedly polarized." (Townsend on Page 119) If neutrinos can be polarized, what is oscillating? Do other particles with mass exhibit polarization?- wotanub
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
Z
Polarization of light after being totally reflected
Homework Statement A circularly polarized light hit the boundary between 2 regions at 45 degree and is totally reflected. What is the polarization state of the reflected beam? Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution Since both s and p component are totally reflected...- Zolo
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Light Polarization
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
S
What is the intensity of light after removing the second polarizer?
Homework Statement Three polarizing filters are stacked, with the polarizing axis of the second and third filters at 23.0° and 62.0°, respectively, to that of the first. If unpolarized light is incident on the stack, the light has intensity 75.0 W/cm^2 after it passes through the stack. If...- srwilliams444
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Light Polarization
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
N
Polarization of photon-Peskin and Schroeder
Hi, I am currently studying quantum field theory with worldwidely used text written by Peskin and Schroeder. On page 165 of that text it says, " the amplitude vanishes unless the final photon is right-handed." But I cannot figure out how it works. With ε = (0,1,i,0), I get same expression...- ndcat10
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Polarization Schroeder
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
A
Is the Transmission Probability of a Vertically Polarized Photon Really 1.0?
I think I understand this only up to a point. 1. Photon spin is quantized to be +1 or -1 and these represent left- and right-hand circular polarization. 2. A photon can have a superposition of 2 spin states in any proportion. 3. Having probability amplitude of 0.5 of spin 1 and 0.5 of spin -1...- Alfred Cann
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Photon Polarization Spin
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

Polarization modulation spectrum
hello all. If one uses polarization modulation of radio waves does this imply a broad frequency spectrum knowing the carrier frequency and amplitude remain the same only the direction of the electric field is being changed ?- jk22
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electrical Engineering
-

Exploring Light's Polarization States: Longitudinal, Temporal, and Scalar
I heard that light in a medium can have longitudinal polarization i.e the e field in the direction of propagation, but i saw in a qed course that light can have temporal or scalar polarization (the E0 component). What is that one and how can one obtain this kind of polarization experimentally ...- jk22
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Light Polarization States
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Optics
-
S
Linear Polarization Experiment Question
I'm a grad student and I got some recent results that I can't figure out. Thought I would post a question and see if I can get a quick answer. I'm taking pictures of polarized system. Using a normal linear polarized filter that has a slip ring, so I take a picture, rotate the slip ring a... -
G
Plane wave equation of linear polarization
Question 1 Basically I have no idea how to calculate the z part of the equation since x and y are assumed to be propagating in the z direction.- geft
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-
S
Direction of nonlinear polarization
Homework Statement A linearly-polarized electromagnetic wave with a frequency w and with an intensity of 1MW/cm2 is propagating in x-direction in a nonlinear crystal with a refractive index n=1.5. Assume that a second-order nonlinear optical susceptibility tensor for second-harmonic...- snickersnee
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
C
Polarization states directly measured : What did this experiment do?
Polarization states "directly measured": What did this experiment do? I ran across, on phys.org, this fairly pop-sciencey RIT press release: http://www.rochester.edu/news/show.php?id=5692 It describes an experiment which sounds very interesting, but the way the experiment is described is...- Coin
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Experiment Polarization States
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
N
Polarization density in a dielectric?
This is polarization density. Can somebody explain to me why exactly this is so? My book just says that's how polarization is defined.. Can you guys give me an intuitive understanding of why? Only thing I know is that χ is related to κ, the dielectric constant, and κ is related to how well a...- Nikitin
- Thread
- Replies: 40
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
V
Polarization of Wave: Learn How to Convert Elliptical into Circular
A linearly polarized wave is one in which the vector sum of electic fields in two perpendicular directions is always directed along the same line. An elliptcal one is that in which the vector sweeps an ellipse, and it can somehow be converted into circular polarization. That is all I understand...- vin300
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Polarization Wave
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Optics
-

Quantum field theory, photons, and polarization.
A circularly polarized electromagnetic wave can be thought of proper combinations of orthogonal linear polarized waves, and a linear polarized wave can be thought of proper combinations of left and right circularly polarized waves. It seems one type of wave is no more fundamental then the other...- Spinnor
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
F
How to Determine the Refractive Index of Glass Using Polarized Light?
Homework Statement Unpolarized light falls on an angle of 37.5 ° with a plan glass surface. The reflected light polarization is examined with a Polaroid. The ratio between maximum and minimum intensity from Polaroid when it is rotated around is 4.0. Which is the refractive of index glass...- fkf
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Polarization Reflection
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
F
How Does Polarization by Reflection Determine the Refractive Index of Glass?
Unpolarized light falls on an angle of 37.5 ° with a plan glass surface. The reflected light polarization is examined with a Polaroid. The ratio between maximum and minimum intensity from Polaroid when it is rotated around is 4.0. Which is the refractive of index glass? I would like to use the...- fkf
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Polarization Reflection
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Optics
-
Y
Polarization and Poincare circle.
What is the theory behind mapping of the latitude and longitude of the sphere in the Poincare Circle to the polarization of the TEM wave? That is, why: 1) Linear polarization when ε=0 deg? 2) Circular polarization when ε=+/- 45 deg? 3) Elliptical when ε is not 0 or +/- 45 deg? 4) RH rotation...- yungman
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Circle Poincare Polarization
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Optics
-
J
Polarization and helicity states
At the beginning of cpt 9, Griffiths states that massive bosons have three polarization states (m_s = 1, 0, -1), but massless ones have only two (m_s = 1, -1). Are these polarization states the same thing as helicity states? I.e. the W/Z would have 3 helicity states and the photon only 2?- JoePhysicsNut
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Helicity Polarization States
- Replies: 1
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
M
Phase difference between polarization and field?
Homework Statement Atomic losses can be described in the Lorentz model by adding into the equation of motion a damping term proportional to velocity. The equation of motion is then \partial ^2x(t) / \partial t^2 + \gamma \partial x(t) / \partial t + \omega_o^2 x(t) = qE/m Consider the optical...- Mixer
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
Y
Using Axial Ratio AR to predict R or L hand polarization.
I take issue with the "Advanced Engineering Electromagnetics" 2nd edition by Balanis again. In Page 156, it claimed for AR=-ve, it is Right Hand rotation, AR=+ve is Left Hand rotation. For plane wave propagates in z direction and at z=0: A)Let Ey lag Ex by \frac{\pi}{2} \Rightarrow\;\vec... -
Y
Question on characterization of elliptical polarization of EM wave.
I am using "Advanced Engineering Electromagnetics" 2nd edition by Balanis AND "Antenna Theory" 3rd edition also by Balanis. I found an inconsistency in how to characterize RHC (CW) and LHC ( CCW) elliptical polarization. 1) In Advanced EE Page 159, for \vec E(0,t)=Re[\hat x...- yungman
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Em Em wave Polarization Wave
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
S
4 nonlinear optics problems: susceptibility, polarization
[Wasn't sure if each problem needed a separate post. Please feel free to edit if needed.] Also \~ and \^ are tilde and hat respectively. 1a. Homework Statement Use perturbation theory to derive the 3rd order nonlinear susceptibility \chi^{(3)}(3w;w,w,w) (problem gives potential energy, etc...- snickersnee
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
2
Help make sense of this polarization explanation by Cal Tech
This vid was produced by Cal Tech. Pay attention to Dr. David Goodstein's explanation of the polarization of light near the end of the video. Does any of it make sense to you, or are Cal Tech Professors showing their fallible sides?- 2112rush2112
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Explanation Polarization
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Optics
-
Y
Verify definition of circular polarization in Balanis.
Attached is a scan of how Balanis define plane wave with circular polarization with Ey having a phase of +∏/2 respect to Ex component of the E field. I don't quite agree with the book. The second attachment is my derivation. The definition of CW or CCW is with respect to direction of... -
I
Electronically controlled polarization of a glass
Hi there, I wonder if anyone heard or read anything about glass where one can control its polarization electronically. Or such that you can switch polarization on and off. Tried to google but all it gives references to polarized glass. Maybe I am using wrong term for such thing? Thanks in...- idaka
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Glass Polarization
- Replies: 1
- Forum: General Engineering
-
Y
Verify my understanding about polarization match of RHC antenna.
I have been trying to understand polarization match in the text from Balanis. The first attachment is the text scanned from the text explaining the polarization of an antenna in RECEIVING mode. I try to understand what the book said and I came up with my interpretation in my writing and drawings...- yungman
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Antenna Match Polarization
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electrical Engineering
-
Y
Please verify my derivation on elliptical polarization of EM wave
This is not a home work, it is part of the textbook on elliptical polarization. Attached is a page in Kraus Antenna book, I cannot verify the equation on the last line. Here is my work E_y=E_2(\sin{\omega} t \cos \delta \;+\; \cos \omega {t} \sin \delta) , \sin\omega {t} =\frac {E_x}{E_1}\;,\...- yungman
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Derivation Em Em wave Polarization Wave
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
P
Plotting the polarization ellipse
Hello, I am tasked with plotting the polarization state of a laser (basically I've made a polarimeter), but I really have no idea where to go at this point. Below is a sample of the program I have written with some real data that I just took from a laser. I have the intensity profile as a...- patmyer1
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ellipse Plotting Polarization
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Optics
-
H
Polarization of white light beam
I want to find out that what happens if we polarize a white light which has all of the wavelenghts of 400-700 (nm).Does it divide into colors?What happens to it?- hamdal
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Beam Light Polarization White light
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Optics
-
T
Describing polarization of a coheret state parametrizing on poincare sphere
The question is here: http://physics.stackexchange.com/questions/45341/representing-a-polarization-vector-for-light-as-a-manifold-of-two-state I'd appreciante any help- TheBlackNinja
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Poincare Polarization Sphere State
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
N
Polarization of Electromagnetic wave
Dear friends i know that a wave is linearly polarized if its components have a phase difference of n*∏ and is circularly polarized if phase difference is n*∏/2. But what if phase difference is neither ∏ nor ∏/2? like for E= ax exp(-j(βy-∏/4)) + azexp(-j(βy-∏/2))... thanks in advance...- najeeb
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
W
Polarization Hysteresis Ciruit
Hi all, I want to measure electric polarization hysteresis loop so i need the electric circuit to measure it. The circuit mostly contains a resistor and a capacitance, i need to what is the exact value of them ? Please tell me if there is a reference for that Thank you- welatiger
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ciruit Hysteresis Polarization
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Materials and Chemical Engineering
-
A
Help for understand of spontaneous polarization in piezo
dear all, I want to confirm whether there is spontaneous polarization in the piezo materials. I know the piezo materials need to be poled under high temperature and electric field before applications. So if there is spontaneous polarization, comes my following confusing. Given a piezo disk with...- athosanian
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Piezo Polarization Spontaneous
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Optics
-
H
Electric polarization of free space
If we take the perspective that free space is permeated with a sea of virtual particles, popping in and out of existence, it seems reasonable that such a sea would experience some amount of electric polarization in the presence of an electric field. That is to say, positively charged virtual...- Hetware
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
R
Polarization of Light After Reflection from Surfaces
I was wondering what happens with linearly polarized light when it is reflected from a surface such as paper? Since it undergoes diffuse reflection, it is scattered in all directions, but does it become randomly polarized, as well? I can't really find an answer to that anywhere, so I'd be... -
R
How to Calculate Flux Density of Light Passing Through Two Parallel HN-32 Sheets
Homework Statement I need some help understanding the following solved problem: If light that is initially natural and of flux density ##I_i## passes through two sheets of HN-32 whose transmission axes are parallel, what will be the flux density of the emerging beam? Solution: ##64 \%...- roam
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Light Polarization
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
Completeness relation for polarization vectors
I'm reading some quantum optics and I stumbled on the following completeness relation for the polarization vectors of the electromagnetic field. \sum_{a} (\epsilon_{\vec{k} a } )_i ( \epsilon^*_{ \vec{k} a} )_j = \delta_{ij} -\frac{k_i k_j}{\vec{k}^2} Does anyone know how to derive...- center o bass
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Polarization Relation Vectors
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
R
Solving Polarization Question for Electric Field in Spherical Shell
A thick spherical shell (inner radius a, outer radius b) is made of dielectric materials with a "frozen-in"polarization P(r) =k/r rhat; where k is a constant and r is the distance from the centre. There is no free charge. Find the electric field E in all three regions by two different...- rbnphlp
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Polarization
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Optics
-
Electric polarization of a dielectric due to a magentic field
Imagine a dielectric cylinder placed in a uniform magnetic field parallel to its axis. Then we make it rotate around its axis. The nuclei and electrons should feel a radial lorentz force because of their rotation around the axis of cylinder.The forces applied to electrons and nuclei are in...- ShayanJ
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
Z
Welcome Exploring Wave Numbers and Polarization
Hi folks, I am new to the group. I was willing to know what is the importance of polarization and also wave number? What idea does angular wave number and general wave number provides? Hope to hear from you guys,soon. Thanks in advance.- zakee.fancy
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Numbers Polarization Wave Welcome
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Other Physics Topics