- #1
manal950
- 177
- 0
A radiator in a domestic heating system operates at a surface temperature of 55 C.
Determine the rate at which it emits radiant heat per unit area if it behaves as a black body ?
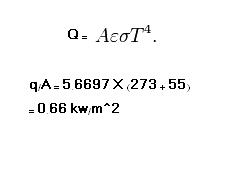
why we did not square the temperature
I mean ( 273 + 55)^4
please I need your help
Determine the rate at which it emits radiant heat per unit area if it behaves as a black body ?
why we did not square the temperature
I mean ( 273 + 55)^4
please I need your help