- #1
mchei
- 7
- 0
i am confused on the determination of zero force member
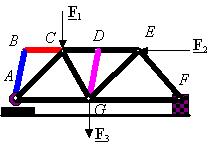
from the above pic, the coloured beam is zero member, i know that when u view from joint B, 2 beams are zero member, but when u view from A, beam_AB is not zero, are there any contradiction?
also, i don't know why when F_AB is zero, then F_BC is also zero? becoz the beam BC don't have any supporting foce on it, am i correct?
finally, i have found 2 rule on wiki but i am confused on it.
do zero force member must not exist when u view the joint that is applied a load or it is a supporting point?
furthermore, is zero force member have zero force acting on it?
2. Homework Equations
1. If only two members meet in an unloaded joint, both are zero-force members.
2. If three members meet in an unloaded joint of which two are in a direct line with one another, then the third (perpendicular) member is a zero-force member.
3. If two members meet in a loaded joint and the line of action of the load coincides with one of the members, the other member is a zero-force member.
3. The Attempt at a Solution
coloured beam is zero force member
from the above pic, the coloured beam is zero member, i know that when u view from joint B, 2 beams are zero member, but when u view from A, beam_AB is not zero, are there any contradiction?
also, i don't know why when F_AB is zero, then F_BC is also zero? becoz the beam BC don't have any supporting foce on it, am i correct?
finally, i have found 2 rule on wiki but i am confused on it.
do zero force member must not exist when u view the joint that is applied a load or it is a supporting point?
furthermore, is zero force member have zero force acting on it?
2. Homework Equations
1. If only two members meet in an unloaded joint, both are zero-force members.
2. If three members meet in an unloaded joint of which two are in a direct line with one another, then the third (perpendicular) member is a zero-force member.
3. If two members meet in a loaded joint and the line of action of the load coincides with one of the members, the other member is a zero-force member.
3. The Attempt at a Solution
coloured beam is zero force member
Last edited: