- #1
HarryLime
- 3
- 0
Summary:: accelerometer Vs gyroscope - measuring torque
Torque can be measured with an accelerometer (tangential-acceleration):
t = F*r and F=m*a, so we get a from the accelerometer, giving:
t = m*a*r Nm
Torque can be measured with an gyroscope (angular-acceleration):
t = F*r
The relationship between tangential (a) to angular (omega) acceleration:
[OK gyroscope gives angular-velocity, so differentiate this once and you get angular-acceleration]
a = omega*r m / s^2
Giving:
t = m*(omega*r)*r = m*r^2 * omega
or if we include the moment of inertia:
t = I*omega
Questions:
[1] Is the assessment correct, Torque can be measured with an accelerometer OR with a gyroscope?
[2] what are the pros and cons of either method?
This seems to sum it up nicely:
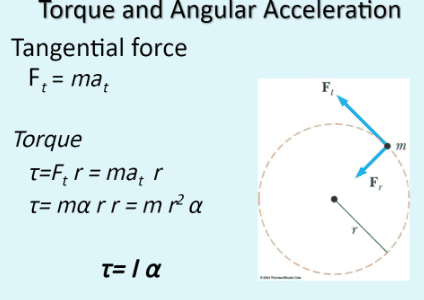
Torque can be measured with an accelerometer (tangential-acceleration):
t = F*r and F=m*a, so we get a from the accelerometer, giving:
t = m*a*r Nm
Torque can be measured with an gyroscope (angular-acceleration):
t = F*r
The relationship between tangential (a) to angular (omega) acceleration:
[OK gyroscope gives angular-velocity, so differentiate this once and you get angular-acceleration]
a = omega*r m / s^2
Giving:
t = m*(omega*r)*r = m*r^2 * omega
or if we include the moment of inertia:
t = I*omega
Questions:
[1] Is the assessment correct, Torque can be measured with an accelerometer OR with a gyroscope?
[2] what are the pros and cons of either method?
This seems to sum it up nicely: