- #1
Eitan Levy
- 259
- 11
Homework Statement
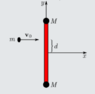
Two bodies with an equal mass of M are attached by a pole with no mass with a length of L. The system is placed on a horizontal table and at first it is at rest. At t=0 a bullet with a mass of m hits the pole, as described in the picture. The collision is completely elastic.
Homework Equations
Momentum conservation.
Angular momentum conservation.
Energy conservation
The Attempt at a Solution
Typing math here is a nightmare for me so I will attach a picture explaining what I tried:
Thanks a lot.