- #1
inv4lid
- 19
- 0
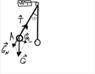
A ball of 100g, suspended from a pulley of a dynamometer, oscillates freely. The length of the pendulum thus obtained is 1m. What are the indications of the dynamometer when the ball is at the point A of it's trajectory? The maximum offset angle is 15 degrees.
Homework Equations
α - alpha (angle), G - gravity, T - restoring force[/B]
m= 0,1 kg.
l = 1m.
α = 15 degrees
_________________|
Sum of all forces (probably, not sure)
Attempts of solving:
If I'm not wrong, there are 2 components of acceleration:
One that moves the object towards the equilibrium state mostly horizontally and one vertically.
The normal component is vertical one, the tangential is horizontal.
Gt = mat
Gsin α = mat
sin 15 degrees = 0.26
at = 2,6 (m/s2)
G = mg = 1;
Gt = 0,26 (N) (=mat)
GN = 0,74 (N)
T-GN = maN
T - 0,74 = 0,1aN
Any tips on how to get T or normal component of acceleration?
Attachments
Last edited: