- #1
Matthew Titus
- 10
- 0
1. The problem statement, all variables, and given/known data
Good day
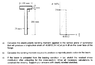
I am preparing for a strength of materials exam and I can't seem to solve this problem. I am unsure if the section below the neutral axis is fully plastic before the edge of the flange experiences the yield stress. Could anyone please provide an explanation or methodology into solving this problem.
summing compressive and tensile forces/moments in order to resolve where the neutral axis has shifted but to be able to do this we would have to assume that the section is entirely plastic below the neutral axis to have one unknown variable which we are not comfortable assuming
Good day
I am preparing for a strength of materials exam and I can't seem to solve this problem. I am unsure if the section below the neutral axis is fully plastic before the edge of the flange experiences the yield stress. Could anyone please provide an explanation or methodology into solving this problem.
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
summing compressive and tensile forces/moments in order to resolve where the neutral axis has shifted but to be able to do this we would have to assume that the section is entirely plastic below the neutral axis to have one unknown variable which we are not comfortable assuming