- #1
Jason C
- 1
- 0
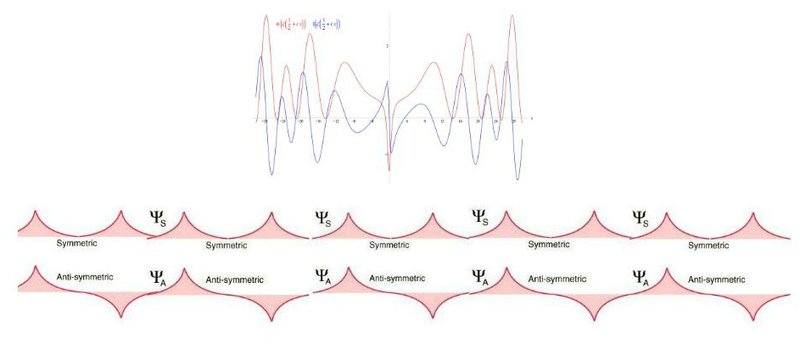
In a recent article by BBM in Physical Review Letters highlights another approach to link QM to Zeta to Prove R.H. There approach proved unsuccessful. I want to ask professional Physicists if the following new approach have merit in connecting the Zeta function to QM? This new line of attack is interpreting the wave graph of ζ(½+it) of Zeta as a wave function. Those wave curves in the graph of ζ(½+it) could be describing the atomic nuclei the Eigenvalue(nontrivial zeros) are related to. It is a new Complex version of the Parity Operator and it is Hermitian. It's eigenvalues can mirror the nontrivial zeros of Zeta. Could this wave function interpretation of ζ(½+it) be the new approach in proving Riemann Hypothesis using Physics? The jpeg attachments are visual representations of this new line of attack for proving RH.