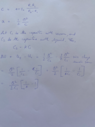- #1
ssarpal
- 7
- 1
- Homework Statement
- An isolated Capacitor is made of a solid conducting sphere of radius R1 and charge +Q surrounded by a conducting spherical shell of inner radius R2 and charge -Q. Initially, the gap between the sphere and the shell has vacuum. Later it is filled with a liquid which has a dielectric constant, K.
For diagram, refer to Fig 8.6 in Section 8.1 Capacitors and Capacitance of University Physics Vol 2 here ...
https://openstax.org/books/university-physics-volume-2/pages/8-1-capacitors-and-capacitance
By how much does the energy change when the liquid is added? Does it increase or decrease?
- Relevant Equations
- From the same section of the book, eq 8.4 gives the Capacitance of a sphere,
𝐶 = 𝑄/𝑉 = 4𝜋𝜀0 * 𝑅1𝑅2/(𝑅2−𝑅1)
Energy stored in a Capacitor is
U = Q^2/2C
I have attached my solution.
Unfortunately, after plugging in the values, my answer is 4 times more than the expected one. What am I missing?
Unfortunately, after plugging in the values, my answer is 4 times more than the expected one. What am I missing?