- #1
ChiralSuperfields
- 1,216
- 132
- Homework Statement
- Please see below
- Relevant Equations
- Please see below
For this problem,
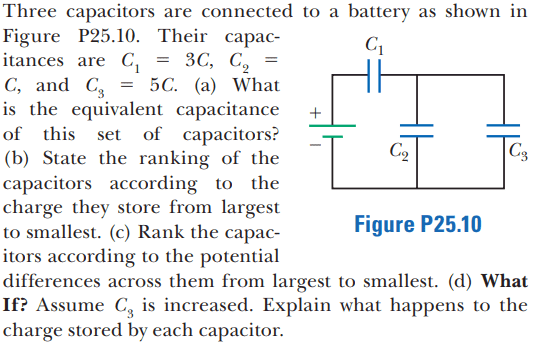
The solution is,
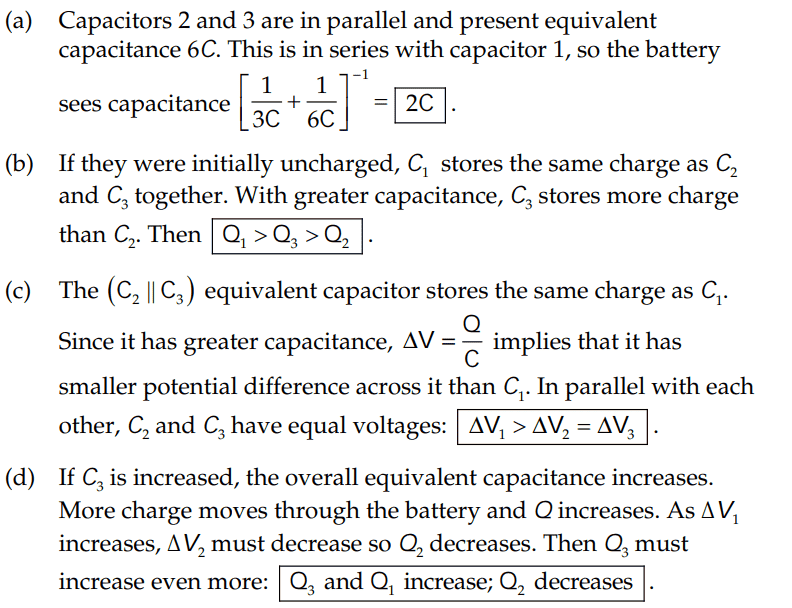
I have a few questions about parts of the solutions,
- Part(b):
(1) Why do they assume that the capacitors are initially uncharged? Do they even need to make that assumption because it seems clear to me that we are finding the charge stored by each capacitor once the circuit has reached steady state. Would it not be better to say assume capacitors ##C_1##, ##C_2## and ##C_3## are charged?
(2) How did they get ## Q_1 > Q_3 > Q_2 ##? I don't understand their statement about if the capacitors are initially uncharged then ##C_1## stores the same charge as ##C_2## and ##C_3## in steady state. I though the answer should be ##Q_2 < Q_1 < Q_3 ## as it should be in the order from smallest to largest capacitance since ##Q ∝ C## (from ##C = \frac {Q}{V}##), correct?
- Part(d):
(3) I don't understand why the charge ##Q## increases from ##Q_i## to ##Q_f##. I thought charge would be conserved in this circuit, why is it not conserved?
Many thanks!
The solution is,
I have a few questions about parts of the solutions,
- Part(b):
(1) Why do they assume that the capacitors are initially uncharged? Do they even need to make that assumption because it seems clear to me that we are finding the charge stored by each capacitor once the circuit has reached steady state. Would it not be better to say assume capacitors ##C_1##, ##C_2## and ##C_3## are charged?
(2) How did they get ## Q_1 > Q_3 > Q_2 ##? I don't understand their statement about if the capacitors are initially uncharged then ##C_1## stores the same charge as ##C_2## and ##C_3## in steady state. I though the answer should be ##Q_2 < Q_1 < Q_3 ## as it should be in the order from smallest to largest capacitance since ##Q ∝ C## (from ##C = \frac {Q}{V}##), correct?
- Part(d):
(3) I don't understand why the charge ##Q## increases from ##Q_i## to ##Q_f##. I thought charge would be conserved in this circuit, why is it not conserved?
Many thanks!