- #1
Snow_buggy
- 1
- 0
- TL;DR Summary
- Is the diffusion direction from high concentration to low concentration and from high temperature to low temperature?
Hi. I am starting to do a gas mixture simulation. I learn the fundamentals from a paper. (doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/43/2/022001)
For a gas mixture (Fe vapor in Argon), the mole fraction of Fe vapor is calculated by,
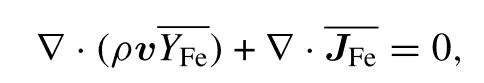 and the diffusion flux JFe is given by,
and the diffusion flux JFe is given by,
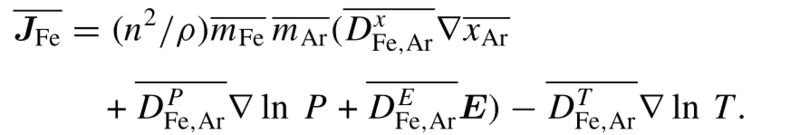
x_ar is the mole fraction of Argon; T is the temperature; P is the pressure; E is the electric field.
It seems like Fe vapor diffuses from high concentration of Fe vapor to low concentration (grad x_Ar) and from high temperature to low temperature (- grad T).
If we calculates the mole fraction of Argon not Fe vapor, this paper (doi: 10.1007/BF01459700) says these coefficients follow this rule,

I don't understand why the temperature diffusion coefficient change the sign? Does it mean the argon diffuses from low temperature to high temperature?
For a gas mixture (Fe vapor in Argon), the mole fraction of Fe vapor is calculated by,
x_ar is the mole fraction of Argon; T is the temperature; P is the pressure; E is the electric field.
It seems like Fe vapor diffuses from high concentration of Fe vapor to low concentration (grad x_Ar) and from high temperature to low temperature (- grad T).
If we calculates the mole fraction of Argon not Fe vapor, this paper (doi: 10.1007/BF01459700) says these coefficients follow this rule,
I don't understand why the temperature diffusion coefficient change the sign? Does it mean the argon diffuses from low temperature to high temperature?