- #1
Travis Enigma
- 13
- 4
- Homework Statement
- A 5.0 g marble is fired vertically upward using a spring gun. The spring must be compressed 8.0 cm if the marble is to just reach a target 20 m above the marble’s position on the compressed spring. (a) What is the change ΔUg in the gravitational potential energy of the marble–Earth system during the 20 m ascent? (b) What is the change ΔUs in the elastic potential energy of the spring during its launch of the marble? (c) What is the spring constant of the spring?
- Relevant Equations
- Ug= mgh
Okay For a this is what I did.
a.
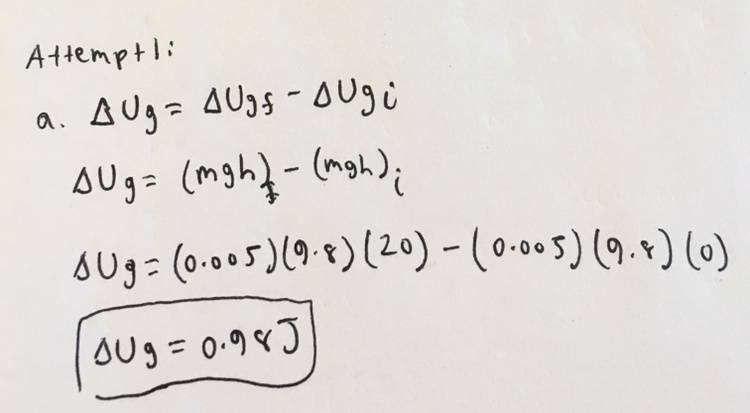
I'm confused about B. I understand that it has something to do with the Conservation of Mechanical Energy, but I don't exactly know what to do.
a.
I'm confused about B. I understand that it has something to do with the Conservation of Mechanical Energy, but I don't exactly know what to do.