- #1
sludger13
- 83
- 0
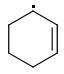
The enthalpies of creating a cyclohexene radical isomers are:
ORTHO: 444 kJ/mol
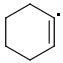
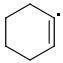
META: 361 kJ/mol
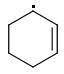
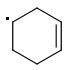
PARA: 401 kJ/mol
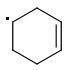
The meta-isomer is most stable (that is the reason for the formation of meta product in radical addition). Para/meta isomers energies seem obvious - both carbons are equivalent, only the meta-carbon participates in multiple bond, para-carbon doesn't.
I can't see why the ORTHO-isomer is the least stable one. The (.CR3) radical should rather be more stable than (.CHR2). What do you think?
ORTHO: 444 kJ/mol
META: 361 kJ/mol
PARA: 401 kJ/mol
The meta-isomer is most stable (that is the reason for the formation of meta product in radical addition). Para/meta isomers energies seem obvious - both carbons are equivalent, only the meta-carbon participates in multiple bond, para-carbon doesn't.
I can't see why the ORTHO-isomer is the least stable one. The (.CR3) radical should rather be more stable than (.CHR2). What do you think?