- #1
andrew1
- 20
- 0
Hi,
I'm having trouble understanding the concept of equivalence classes and would like some help on what it means to describe an equivalence class.
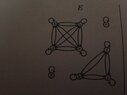
Here is an example that I have deemed to be an equivalence relation but I have no idea about how I can descrive its equivalence class
View attachment 2405
I'm having trouble understanding the concept of equivalence classes and would like some help on what it means to describe an equivalence class.
Here is an example that I have deemed to be an equivalence relation but I have no idea about how I can descrive its equivalence class
View attachment 2405
Attachments
Last edited: