- #1
- 2,486
- 9,719
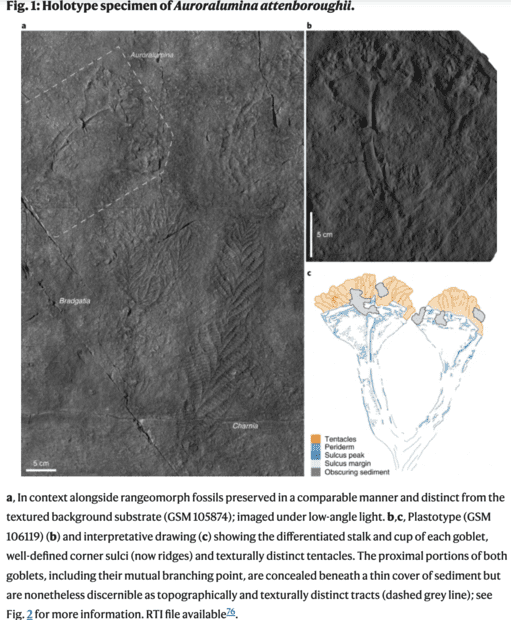
Fossils of a new jellyfish relative from 635 to 541 MYA has been found in the Charnwood Forest, a hilly area of Leicestershire in central England. This is a place where Ediacaran (PreCambrian) fossils have been found before and where David Attenborough would look for fossils as a kid. Guess he missed these but they named it after him anyway (Auroralumina attenboroughii). The Auroralumina part of the name refers to its early location in the fossil record (Aurora means dawn) and it similarity in shape to an olympic tourch (lumina means light).
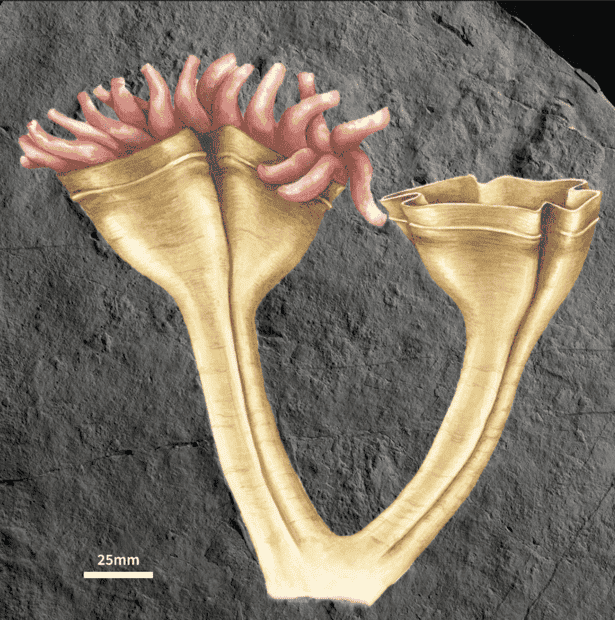
reconstruction
Here is a Science magazine news article on it.
Here is the research non-paywalled Nature Ecology and Evolution article on it.
Cnidarian are among the earliest and simplest of animal body plans. It is generally a continuous epithelial layer folded into an outer body layer, an inner digestive layer that connects with the outer layer at the mouth (which also acts as an anus to eject undigested food), and some thin tentacles projecting out from around the mouth. They also have stinging cells (nematocysts) a specialist cell type not found in other metazoans (animals).
Ediacaran animal fossils are structurally simpler than known animals, except for trace fossils indicative of a bilateral worm-like thing.
This is the first Ediacaran fossil that can be reasonably connected with an existing animal group.
reconstruction
Here is a Science magazine news article on it.
Here is the research non-paywalled Nature Ecology and Evolution article on it.
Cnidarian are among the earliest and simplest of animal body plans. It is generally a continuous epithelial layer folded into an outer body layer, an inner digestive layer that connects with the outer layer at the mouth (which also acts as an anus to eject undigested food), and some thin tentacles projecting out from around the mouth. They also have stinging cells (nematocysts) a specialist cell type not found in other metazoans (animals).
Ediacaran animal fossils are structurally simpler than known animals, except for trace fossils indicative of a bilateral worm-like thing.
This is the first Ediacaran fossil that can be reasonably connected with an existing animal group.