- #1
Esearcher
- 1
- 0
Member has been warned to show more of their own effort and no to remove the template.
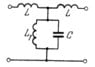
Need the dispersion equation for chain consisting of cell units ( LC unit scheme in attachments).
I know I need to make complex Kirchhoff equations and after get the dispersion equation but absolutely don't know how to do it. All examples that I find in web very poor including books, articles. I learn electrical engineering a little little bit and this also definitely prevents me from solving this problem.
Also attached the answer (which i can't get)
I know I need to make complex Kirchhoff equations and after get the dispersion equation but absolutely don't know how to do it. All examples that I find in web very poor including books, articles. I learn electrical engineering a little little bit and this also definitely prevents me from solving this problem.
Also attached the answer (which i can't get)