- #1
Kovac
- 13
- 2
Thread moved from the technical forums to the schoolwork forums
TL;DR Summary: .
I need to find the location of following bodies MMR with Jupiter: 4:1, 3:1, with the help of Keplers third law.Keplers third law:
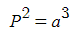 , where P is the orbital period in Earth years, a= semi major axis in AU.
, where P is the orbital period in Earth years, a= semi major axis in AU.
For Jupiter: Pj =
 years.
years.
Now my question is, to find the location of 4:1, should I simply take 1/4 * Pj as the new P? (Since 4 orbits are made with each Jupiter orbit)
And then use the formula again with
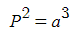 to find the position for a? Meaning I need to solve for a with the new P?
to find the position for a? Meaning I need to solve for a with the new P?
I need to find the location of following bodies MMR with Jupiter: 4:1, 3:1, with the help of Keplers third law.Keplers third law:
For Jupiter: Pj =
Now my question is, to find the location of 4:1, should I simply take 1/4 * Pj as the new P? (Since 4 orbits are made with each Jupiter orbit)
And then use the formula again with