- #1
Grandpa04
- 2
- 3
- Homework Statement
- A circular solenoid has a magnetic field of 1.4 T. The solenoid has 900 turns, a radius of 2 cm, and a length of 70 cm. What is the current running through the solenoid.
- Relevant Equations
- B = µ*N*I/2πr
I assumed that the radius is referring to a major R like in the image below.
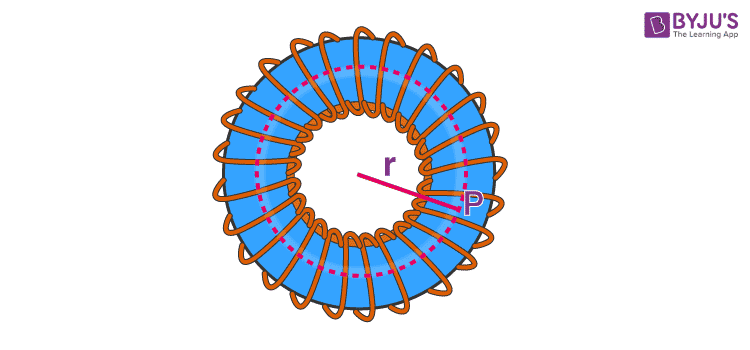
I plugged all the values (except for length) into the equation B = µ*N*I/2πr to get 155.6 A for the current value. I am unsure if this is the correct value or if radius refers to minor r of solenoid, in which case a different equation is used.
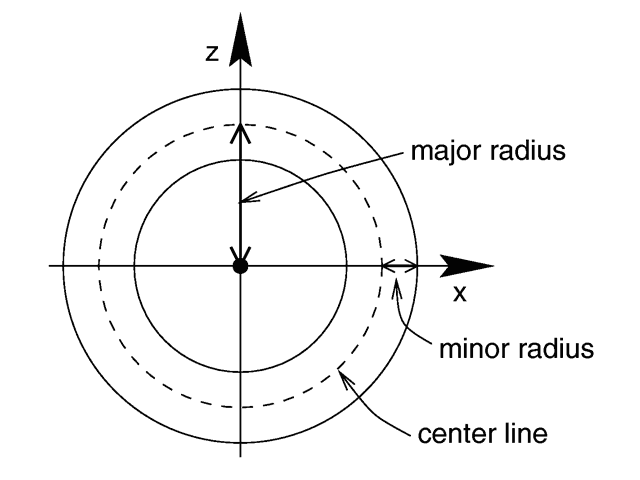
I plugged all the values (except for length) into the equation B = µ*N*I/2πr to get 155.6 A for the current value. I am unsure if this is the correct value or if radius refers to minor r of solenoid, in which case a different equation is used.