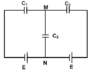
- #1
Gourab_chill
- 55
- 3
- Homework Statement
- I have been asked to find the potential difference between points M and N in the given figure. The circuit is in the attachment.
- Relevant Equations
- Q=CV
I tried to attempt it by applying KVL to both the loops.

I tried to find a possible charge distribution for the capacitors. I guess this is right.
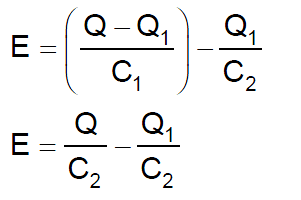
On solving I get:
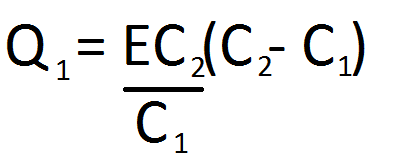
from what I know potential difference between M and N is Q1/C2
but the solution is given as:

Where am I wrong?
I tried to find a possible charge distribution for the capacitors. I guess this is right.
On solving I get:
from what I know potential difference between M and N is Q1/C2
but the solution is given as:
Where am I wrong?