- #1
spaghetti3451
- 1,344
- 33
The momentum-space fermion propagator in the free Dirac theory is given by
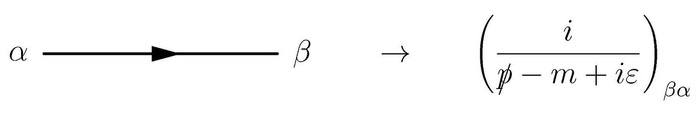
The arrow on the fermion propagator is said to represent the flow of charge.
How can we derive this statement quantitatively from the Dirac Lagrangian?
What is the quantitative form of the charge being referred to here?
The arrow on the fermion propagator is said to represent the flow of charge.
How can we derive this statement quantitatively from the Dirac Lagrangian?
What is the quantitative form of the charge being referred to here?