- #1
songoku
- 2,294
- 325
Homework Statement
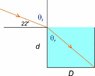
1. A cylindrical tank 2.4 m deep is full to the brim with water. Sunlight first hits part of the tahnk bottom when the rising maes at 22o angle with the horizon. Find the tank's diameter
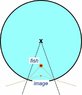
2. An aquarium is made from a thin-walled tube of transparent plastic 50 cm in diameter. If we are looking directly into th aquarium, what is the apparent distance to a fish 15 cm from the aquarium wall?
Homework Equations
n = c / v
n1sin i = n2 sin r
n = real depth / apparent depth
The Attempt at a Solution
1. I can't imagine the situation and I don't understand this part :"Sunlight first hits part of the tank bottom when the rising makes at 22o angle with the horizon."
2. The shape of the aquarium is cylindrical? I don't know what the diameter is used for.
Please help. Thanks