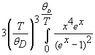- #1
acherentia
- 48
- 0
Homework Statement
In Atkins's physical chemistry textbook it is written that Debye considered atoms to oscillate from 0 up to a nu max. It is explained further in the text that the complication (i.e., not all atoms oscillating at same frequency as shown in Einstein's formula) is accounted for, by averaging over all the frequencies present.
An average is not a maximum however?! How did he measure the frequencies that were present so as to get the average?
Homework Equations
attached