- #1
sicro
- 8
- 0
Hello!
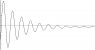
I have data of a damped oscillation (the movement on Y as it dies down in time). Imagine for example a ball that is hanging from a spring and it keeps bouncing up and down under the spring until it stops.
The problem is I do not know how to find the axis around which the oscillation happens.
I need to subtract or add A VALUE to the data I have for the Y points in order to centre the data around an axis -the axis of oscillation-. How do I find out how much to add or subtract?
I tried to find the median of the data points for Y and subtract/add that from the data... It works but it doesn't work well enough. I know that it doesn't work well enough because the curve of decay for the points of the peaks has a slightly different exponent for e than the curve of decay for the troughs (* -1).
PS: I do not have the Y point where the oscillation stops, as the data gathering stopped before a complete stop of the system.
Thank you!
I have data of a damped oscillation (the movement on Y as it dies down in time). Imagine for example a ball that is hanging from a spring and it keeps bouncing up and down under the spring until it stops.
The problem is I do not know how to find the axis around which the oscillation happens.
I need to subtract or add A VALUE to the data I have for the Y points in order to centre the data around an axis -the axis of oscillation-. How do I find out how much to add or subtract?
I tried to find the median of the data points for Y and subtract/add that from the data... It works but it doesn't work well enough. I know that it doesn't work well enough because the curve of decay for the points of the peaks has a slightly different exponent for e than the curve of decay for the troughs (* -1).
PS: I do not have the Y point where the oscillation stops, as the data gathering stopped before a complete stop of the system.
Thank you!
Attachments
Last edited: