- #1
ElPimiento
- 17
- 0
Hi,
(This is more of a math question but I thought Astronomy people would be more familiar with the equation and how it's used)
So in Monaghan 1992 (http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1992ARA&A..30..543M, bottom of pg 554) a cubic spline in three dimensions is defined. I tried to integrate it (using a triple integral in spherical coordinates), expecting to get 1 but got ##3\pi/4h^2##. Are there special considerations that need to be taken into account when your integrating this function? Here's my work:
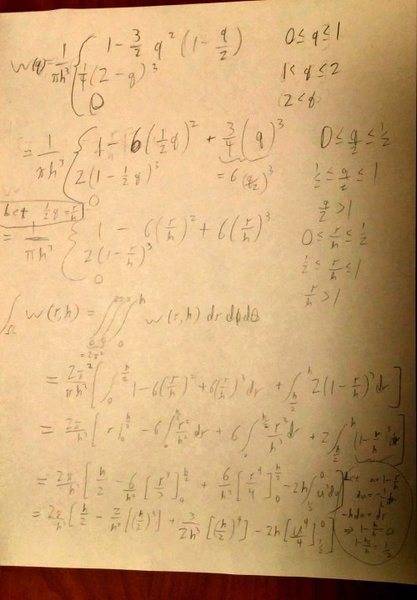
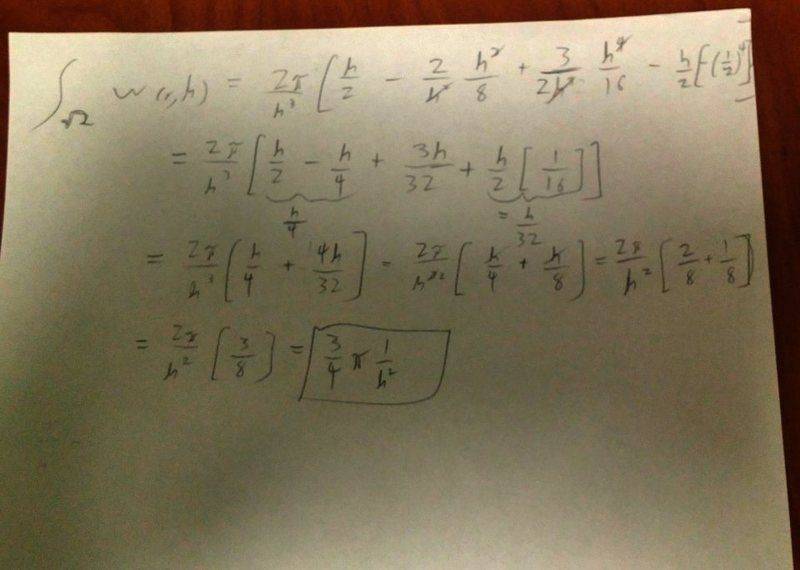
(I tried to make the writing easier to see by fiddling with the contrast, it kind-of worked)
(Also, I'm an Undergrad doing research so I didn't know what level to make the thread ... I or A ... )
Thanks,
- Andrew
(This is more of a math question but I thought Astronomy people would be more familiar with the equation and how it's used)
So in Monaghan 1992 (http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1992ARA&A..30..543M, bottom of pg 554) a cubic spline in three dimensions is defined. I tried to integrate it (using a triple integral in spherical coordinates), expecting to get 1 but got ##3\pi/4h^2##. Are there special considerations that need to be taken into account when your integrating this function? Here's my work:
(I tried to make the writing easier to see by fiddling with the contrast, it kind-of worked)
(Also, I'm an Undergrad doing research so I didn't know what level to make the thread ... I or A ... )
Thanks,
- Andrew