- #1
Gwinterz
- 27
- 0
Hi,
I just have some questions regarding the use of beam displacers, the below picture pretty neatly summarises what they do:
http://www.fiberoptics4sale.com/Merchant2/graphics/00000001/What-is-Optical-Circulator-and-its-Appli_F29F/image_8.png
My question is, what happens when polarised light enters from the right, in the above picture:
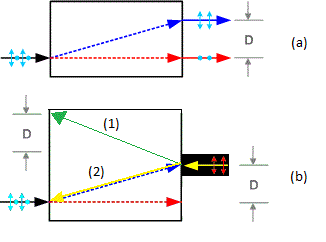
Figure (a) depicts a normal beam displacer while Figure (b) is an attempt at depicting my question. I left the original blue/red lines to make a more clear comparison with (a). In Figure (b) vertically polarised enters the beam displacer in the same position that vertically polarised light would exit, in Figure (a). My question is, does the beam follow paths (1), (2), or a mixture of both? That is, does the beam displacer again displaced the vertically polarised light upward by distance D or does the light (for some reason) follow path (2) where it is displaced downward. Intuitively I would have thought that path (1) is what would happen but I just wanted to ask here to be sure.
Another way to ask this question is, considering the first picture I posted and Figure (a), if the beam displacer was placed back to front, i.e. flipped horizontally, would the unpolarised light be displaced in the same manner?
Thanks in advanced
I just have some questions regarding the use of beam displacers, the below picture pretty neatly summarises what they do:
http://www.fiberoptics4sale.com/Merchant2/graphics/00000001/What-is-Optical-Circulator-and-its-Appli_F29F/image_8.png
My question is, what happens when polarised light enters from the right, in the above picture:
Figure (a) depicts a normal beam displacer while Figure (b) is an attempt at depicting my question. I left the original blue/red lines to make a more clear comparison with (a). In Figure (b) vertically polarised enters the beam displacer in the same position that vertically polarised light would exit, in Figure (a). My question is, does the beam follow paths (1), (2), or a mixture of both? That is, does the beam displacer again displaced the vertically polarised light upward by distance D or does the light (for some reason) follow path (2) where it is displaced downward. Intuitively I would have thought that path (1) is what would happen but I just wanted to ask here to be sure.
Another way to ask this question is, considering the first picture I posted and Figure (a), if the beam displacer was placed back to front, i.e. flipped horizontally, would the unpolarised light be displaced in the same manner?
Thanks in advanced
Last edited by a moderator: