- #1
chwala
Gold Member
- 2,650
- 351
- Homework Statement
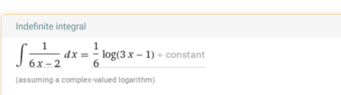
- How do we deal with the integration of $$\int \dfrac{1}{6x-2} dx?$$
- Relevant Equations
- Natural logs integration
This is a bit confusing...conflicting report from attached wolfram and symbolab. Which approach is correct?
Attachments
Last edited: