- #1
jfulky
- 3
- 1
Homework Statement
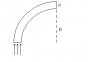
3. A fiber optic cable is essentially a thin fiber of plastic with n = 1.46, surrounded by a protective material with n = 1.32. The light can travel around a bend in the fiber if it can internally reflect inside the fiber. If the diameter of the fiber is d = 0.900 mm find the smallest inner radius of curvature, R, into which the fiber can be bent that will allow light that is initially traveling parallel to the fiber to remain inside the fiber.
Homework Equations
Sin(Θ)c = n1/n2
The Attempt at a Solution
My work is in the thumbnail. I am not entirely sure how to approach this problem. My though process was to find the critical angle in which the light is internally reflected, and then use geometry to find the radius of curvature, since I am not sure of any more equations that would help me. I also though of using arc length in some way, to relate the distance the light traveled in the tube to the circumference of the circle.
Any help would be appreciated!